Jagran Josh
All Formulas of Physics for Class 10: Here you will find all the Class 10 Physics formulas. Download the lens formula, mirror formula, potential difference, magnification, Snell’s law of refraction, and electricity formulas PDF.
Physics Formulas for Class 10 Students: Physics is one of the most important and difficult subjects. For many students, it is like an academic ghost. As you grow and enter senior high school, the level of physics formulas and its concepts becomes difficult to learn. Especially for Class 10 students who will face the board exams for the first time, learning physics formulas is one of the most complicated tasks. If you know all the formulas, then consider half of the syllabus done.
Read: Class 10 Science Syllabus 2023–24
Here you will find all the formulas for Physics Class 10. The formulas are covered for topics such as light reflection and refraction, electricity, and magnetism. Lens formulas, mirror formulas, potential differences, magnification, Snell’s law of refraction formulas, etc. are discussed here. You can read and download the free physics formula PDF here. Check out the formulas below.
Light – Reflection and Refraction Formulas
For Class 10 students, this topic is very important, as they will study the same in Class 12 physics. Your foundation in Class 10 physics will definitely help you in your Class 12 physics optics. The mirror formula, lens formula, and magnification formula are some of the important ones that should be remembered to solve all the numerical problems related to light, reflection, and refraction in Class 10 board exams. Check out the formulas below.
Read: CBSE Class 10 Physics Chapter Wise Important Questions and Answers for 2023
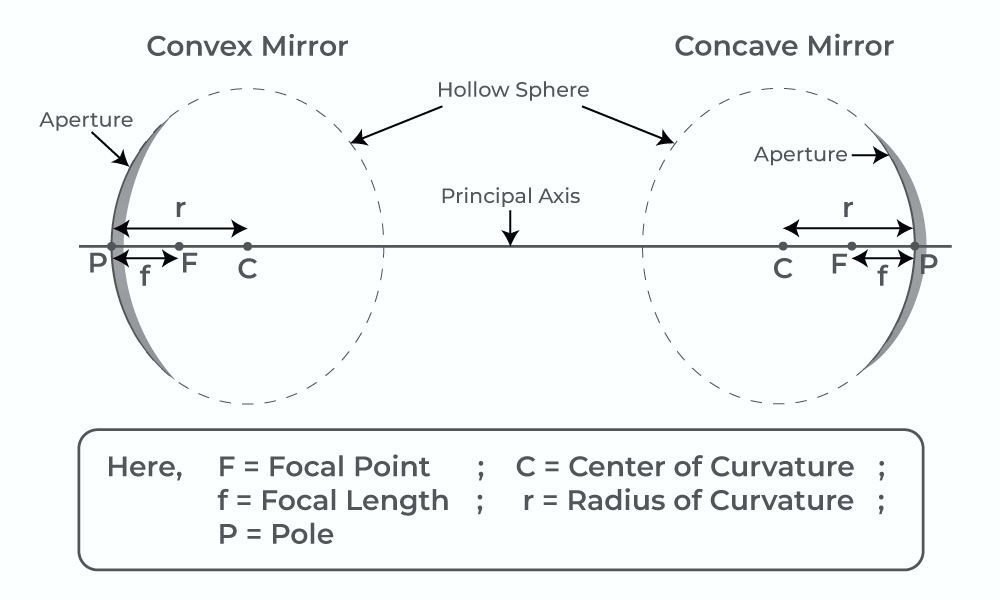
Radius of curvature (R)
R= 2f
f= Focal length
The distance between the pole and the principal focus of a spherical mirror is called the focal length.
Focal length (f)
f=R/2
R= Radius of curvature
The radius of curvature is the distance between the centre of a curved surface and its curvature.
Mirror Formula
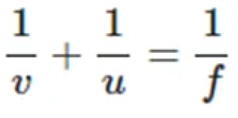
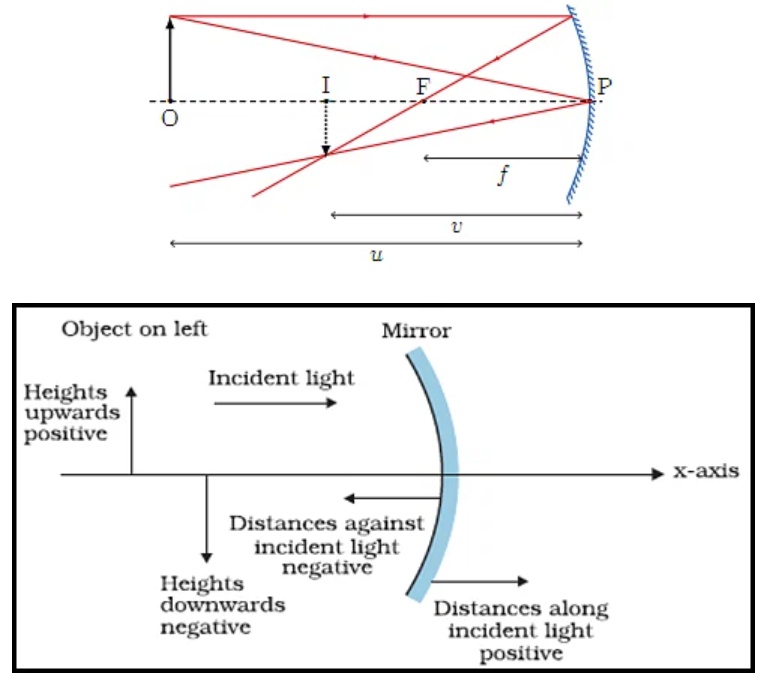
v= The distance of the image from the pole of the mirror is called the image distance.
u= The distance of the object from its pole is called the object distance
f= Focal length
Read: Important Physics Diagrams Class 10
Mirror Magnification
Magnification produced by a spherical mirror gives the relative extent to which the image of an object is magnified with respect to the object size
The magnification m is also related to the object distance (u) and image distance (v). It can be expressed as:

Snell’s law of refraction
(This is true for angle 0 < i <90o)
According to this law, the ratio of the sine of angle of incidence to the sine of angle of refraction is a constant, for the light of a given colour and for the given pair of media.
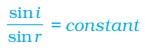
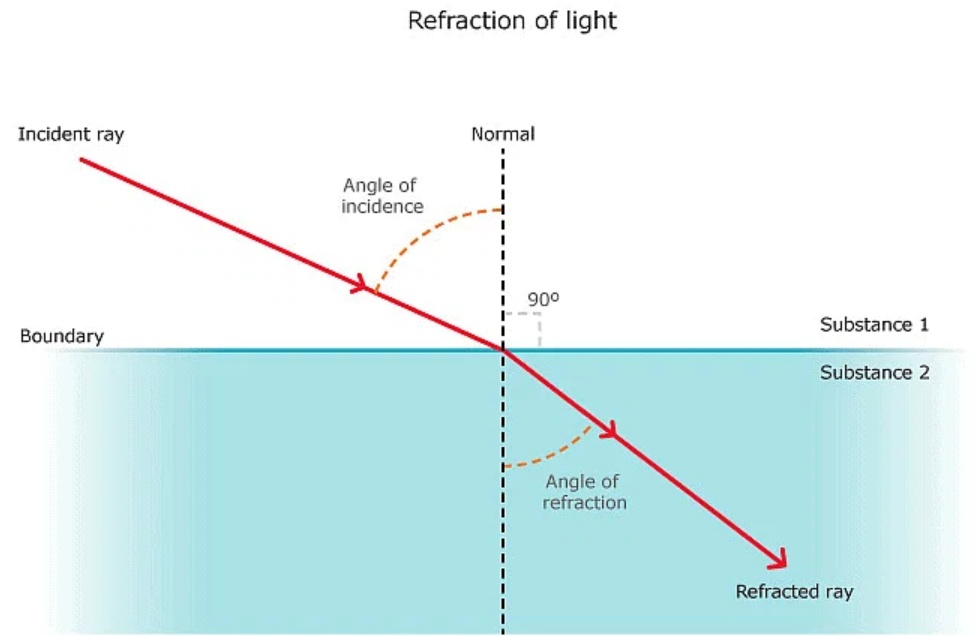
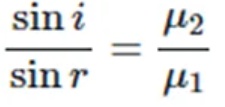
If c is the speed of light in air and v is the speed of light in the medium, then, the refractive index of the medium nm is given by

Lens Formula
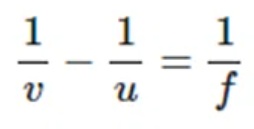
u= Object distance
v= Image distance
f= Focal length
Lens Magnification
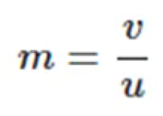
Read: CBSE Class 10 Science Deleted Syllabus 2023-24
Read: Class 10 Science Revision Notes (Based on Revised Syllabus)
Read: CBSE Class 10 Science Sample Paper for Board Exam 2024
Power of Lens
P=1/focal length(f)
Electricity Formulas
Current Formula
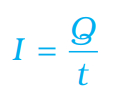
Q= Net charge
I= Current
t= Time
Potential difference
Potential difference (V) between two points = Work done (W)/Charge (Q)
V = W/Q
Ohm’s law
V ∝ I
V = IR
V= Potential difference
I= Current
R= Resistance
Resistance of the conductor
R ∝ l
R ∝ l/A
l= Length
A= Area of cross-section
ρ= (rho) is a constant of proportionality and is called the electrical resistivity of the material of the conductor
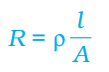
Potential difference (In Series)
V = V1 + V2 + V3
Resistance (In Series)
Rs = R1 +R2 + R3
Current (In Series)
I = I1 + I2 + I3
Resistance (In Parallel)
1/Rp = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3
Power Input
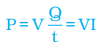
I= Current
V= Potential Difference
t= Time
Q= Charge
Study Current
H = VIt
H= Heat
V= Potential Difference
I= Current
t= Time
Joule’s law of heating
H = I2 Rt
H= Heat
R= Resistance
I= Current
t= Time
Electric Power
P = VI
Or
P = I2R = V2/R
P= Power
I= Current
V= Potential difference
R= Resistance
Also Read:
#Physics #Formulas #Class #Download #TopicWise #PDF
