Jagran Josh
CBSE Class 10 Biology Control and Coordination Important Questions and Answers: This article will cover the important question and answers of the second chapter Control and Coordination under the unit World of Living. Although students will commonly find this as the seventh chapter in various resource materials, according to the latest syllabus by CBSE, it is Chapter 7 Control and Coordination.
Living organisms use systems that provide them control and coordination. In fact, in multicellular organisms, specialised tissues and systems provide these control and coordination to help them perform daily activities.
Chapter 7 Control and Coordination covers topics such as Tropic movements in plants; Introduction of plant hormones; Control and co-ordination in animals: Nervous system; Voluntary, involuntary and reflex action; Chemical co-ordination: animal hormones.
To view the complete syllabus in detail, click on the link below:
Like any other science subjects, biology also pushes students to think logically and critically about the world around us.
Important Questions from CBSE Class 10 Biology Control and Coordination
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Q.1. Which of the following statements is correct about receptors?
(a) Gustatory receptors detect taste while olfactory receptors detect smell
(b) Both gustatory and olfactory receptors detect smell
(c) Auditory receptors detect smell and olfactory receptors detect taste
(d) Olfactory receptors detect taste and gustatory receptors smell
Q.2. Cerebellum is situated in ___________.
- fore brain
- midbrain
- hindbrain
- partly in A and B each
Q 3. In a synapse, chemical signal is transmitted from
(a) dendritic end of one neuron to axonal end of another neuron
(b) axon to cell body of the same neuron
(c) cell body to axonal end of the same neuron
(d) axonal end of one neuron to dendritic end of another neuron
Q.4. A doctor advised a person to take an injection of insulin because——-.
A) His blood pressure was low
B) His heart was beating slowly
C) He was suffering from goitre
D) His sugar level in blood was high
5. Which is the correct sequence of the components of a reflex arc?
(a) Receptors → Muscles → Sensory neuron → Motor neuron → Spinal cord
(b) Receptors → Motor neuron → Spinal cord → Sensory neuron → Muscle
(c) Receptors → Spinal cord → Sensory neuron → Motor neuron → Muscle
(d) Receptors → Sensory neuron → Spinal cord → Motor neuron → Muscle
6. In reflex action, the reflex arc is formed by
- Muscles – receptor – brain
- Muscles – effector – brain
- Receptor – spinal cord – muscles
- Spinal cord – receptor – muscles
7. Posture and balance of the body is controlled by
(a) cerebrum
(b) cerebellum
(c) medulla
(d) pons
Q.8. Damage of cerebellum will mostly affect the career of :
A) architect
B) teacher
C) librarian
D) athlete
Q.9. The movement of shoot towards light is
(a) geotropism
(b) hydrotropism
(c) chemotropism
(d) phototropism
Q.10. The substance that triggers the fall of mature leaves and fruits from plants is due to
- Auxin
- Gibberellins
- Cytokinin
- Abscisic acid
Q.11. Which of the following is not associated with growth of plant?
(a) Auxin
(b) Gibberellins
(c) Cytokinins
(d) Abscisic acid
12.The plant hormone which is essential for cell division is
(A) Ethylene
(B) Auxin
(C) Gibberellin
(D) Cytokinin
Q.13. Choose the incorrect statement about insulin
(a) It is produced from pancreas
(b) It regulates growth and development of the body
(c) It regulates blood sugar level
(d) Insufficient secretion of insulin will cause diabetes
Q.14. The gap between two neurons is known as ___.
(A) synapse
(B) synopsis
(C) impulse
(D) synaptic node
Q.15. The shape of guard cells changes due to change in the
(a) protein composition of cells
(b) temperature of cells
(c) amount of water in cells
(d) position of nucleus in the cells
Q.16. The substance that accelerates the growth in the stem is ____.
- auxin
- cytokinin
- enzyme
- vitamin
Q.17.The growth of pollen tubes towards ovules is due to
(a) hydrotropism
(b) chemotropism
(c) geotropism
(d) phototropism
18. In a synapse, chemical signal is transmitted from
(A) dendritic end of one neuron to axonal end of another neuron
(B) axon to cell body of the same neuron
(C) cell body to axonal end of the same neuron
(D) axonal end of one neuron to dendritic end of another neuron
Q.19. The substance that triggers the fall of mature leaves and fruits from plants is due to
(a) auxin
(b) gibberellin
(c) abscisic acid
(d) cytokinin
Q.20. Growth hormone is produced in ___________.
- hypothalamus
- pituitary
- pancreas
- thyroid
ASSERTION AND REASON TYPE QUESTIONS
Following questions consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions selecting the appropriate option given below:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Q.1. Assertion (A) : Insulin regulates blood sugar level.
Reason (R) : Insufficient secretion of insulin will cause diabetes.
Q.2. Assertion(A): A growing plant appears to bend towards the direction of light
Reason (R) : The plant hormone auxin diffuses towards the shady side of the root.
Q.3. Assertion (A) : The effect of auxin hormone on the growth of root is exactly opposite to that on a stem.
Reason (R) : Auxin hormone increases the rate of growth in root and decreases the rate of growth in stem.
Q.4. Assertion(A) : The use of iodised salt prevents risk of goitre.
Reason (R) : Iodised salt provides iodine needed by thyroid gland to make sufficient thyroxin for our body.
Q.5. Assertion (A) : The brain is also known as the central nervous system.
Reason (R) : Central nervous system controls and regulates the voluntary actions.
Q.6. Assertion (A) : Animals can react to stimuli in different ways.
Reason (R) : All animals have a nervous system and an endocrine system involving hormones.
Q.7. Assertion (A) : A receptor is a specialized group of cells in a sense organ that perceive a particular type of stimulus.
Reason (R) : Different sense organs have different receptors for detecting stimuli.
VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
Q.1. Name two specialised tissues that provide control and coordination in multicellular organisms.
- 2. Write the name and functions of any two parts of the human hind-brain.
- 3. Which part of the nervous system controls reflex arcs?
Q.4. How does a touch – me – not plant respond on touching? What is this movement called?
- 5. Name the sensory receptors found in the nose and on the tongue.
- 6. List two body functions that will be affected if the cerebellum gets damaged.
- 7. Which gland secretes growth hormone in human beings?
SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
Q.1. Name the hormones secreted by the following endocrine glands and specify one function of each:
(a)Thyroid (b) Pituitary (c) Pancreas
Q.2. Write one example each of the following tropic movements :
(i) Positive phototropism (ii) Negative phototropism
(iii) Positive geotropism (iv) Negative geotropism
(v) Hydrotropism (vi) Chemotropism
Q.3. (a) An old man is advised by his doctor to take less sugar in his diet. Name the disease from which the man is suffering. Mention the hormone due to imbalance of which he is suffering from this disease. Which endocrine gland secretes this hormone?
(b) Name the endocrine gland which secretes growth hormone. What will be its effect on a person if there is: (i) Deficiency of growth hormones (ii) Excess secretion of growth hormones?
Q.4. What is Chemotropism? Give one example. Name any two plant hormones and mention their functions.
Q.5. (a) Name the part of brain which controls: (i) voluntary action (ii) involuntary action.
(b) What is the significance of the peripheral nervous system? Name the components of this nervous system and distinguish between the origin of the two.
Q.6. How does chemical coordination occur in plants? Explain with the help of three examples.
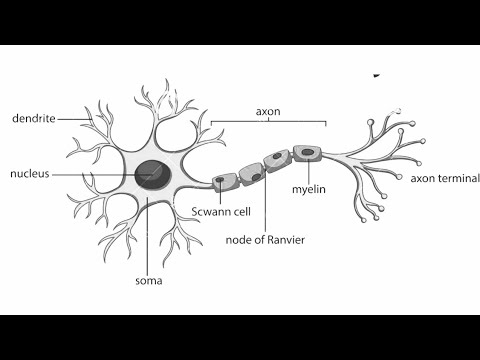
7. Draw and label a Neuron. Explain how it carries messages.
LONG ANSWER QUESTION
Q.1. a) Name chemical messenger of endocrine glands responsible for changes taking place in the body
b) Mention the gland which produces adrenalin and write its function
c) Name two phytohormones
2. Give the function(s) of the following plant hormones:
a. Auxins b. Gibberellins c. Cytokinins d. Abscisic acid e. Ethylene
Q 3. Smita’s father was complaining about frequent urination, pain in legs and a frequent weight loss to Smita’s mother and she discussed the things with her daughter when Smita returned from school. Listening to this Smita told her mother that her father should go and visit a doctor immediately. The doctor diagnosed that Smita’s father was having an elevated level of blood glucose. He should take care of his diet and should exercise regularly to maintain his normal glucose level.
On the basis of the text, answer the following questions:
(i) Name the disease he is suffering from and name the hormone whose deficiency causes it.
(ii) Identify the gland that secretes it and mention the function of this hormone.
(iii) Explain how the time and amount of secretion of this hormone is regulated in human system.
4. Mention one function for each of these hormones.
i) Thyroxine
ii) Insulin
iii) Estrogen
iv) Growth hormone
v) Testosterone.
CASE STUDY QUESTION
1 The human brain is a 3- pound (1.4-kilogram) mass of jelly-like fats and tissues—yet it’sthe most complex of all known living structures The human brain is more complex than any other known structure in the universe. Weighing in at three pounds, on average, this spongy mass of fat and protein is made up of two overarching types of cells—called glia and neurons— and it contains many billions of each. Neurons are notable for their branch-like projections called axons and dendrites, which gather and transmit electrochemical signals. Different types of glial cells provide physical protection to neurons and help keep them, and the brain, healthy. Together, this complex network of cells gives rise to every aspect of our shared humanity. We could not breathe, play, love, or remember without the brain.
1) Animals such as elephants, dolphins, and whales actually have larger brains, but humans have the most developed cerebrum. It’s packed to capacity inside our skulls and is highly folded. Why our brain is highly folded?
2) Which among this is not a function of cerebrum?
- a) speech
- b) Learning
- c) Posture
- d) Emotion
3) Which among these protects our brain?
a)Neurotransmitter
b) Cerebrospinal fluid
c)Meninges
d) Grey matter
i) a, b & c
ii)b & c
iii)c & d
iv) b,c&d
2 All the living organisms (plants and animals) respond and react to changes in the environment around them. The changes in the environment to which the organisms respond and react are called stimuli (singular: stimulus). The living organisms show response to stimuli such as light, heat, cold, sound, smell, taste, touch, pressure, pain, water, and force of gravity, etc. The response of organisms to a stimulus is usually in the form of some movement of their body parts. For example, if a man touches a very hot utensil accidently, he quickly pulls his hand away from the hot utensil. Here, heat is the stimulus and the man reacts by moving his hand away from the hot utensil. Similarly, when the Sun is bright, we close our eyes. In this case, light is the stimulus and we react by closing the eyes.
- Humans respond to changes in their surrounding environment. The changes are known as _
a. activity
b. stimuli
c. action
d. coordination
2. You close your eyes when your friend point the torchlight towards your eye. Which sensory organ is involved?
a. Skin
b. Eyes
c. Nose
d. Tongue
3. A baby cries when hears the thunder. What is the stimulus that is involved?
a. smell
b. sound
c. taste
d. light
4. Based on the situation below, which situation shown human respond to stimuli?
I- A boy pulls his hand when touching a hot object.
II- A girl is reading a book.
III- A girl closes her ear when hearing the thunder.
IV- A boy is walking to school.
a. I and III
b. I and IV
c. II and III
d.II and IV
5. A response is ____
- A change in the environment that causes a reaction
- Something you write on a test
- A reaction to a change in the environment
- The way plants communicate
ANSWER KEY
|
S No |
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS |
|
1 |
A |
|
2 |
C |
|
3 |
D |
|
4 |
D |
|
5 |
D |
|
6 |
C |
|
7 |
B |
|
8 |
D |
|
9 |
D |
|
10 |
D |
|
11 |
D |
|
12 |
D |
|
13 |
B |
|
14 |
A |
|
15 |
C |
|
16 |
A |
|
17 |
B |
|
18 |
D |
|
19 |
C |
|
20 |
B |
|
S No |
ASSERTION AND REASON QUESTIONS |
|
1 |
A |
|
2 |
A |
|
3 |
C |
|
4 |
A |
|
5 |
D |
|
6 |
A |
|
7 |
B |
VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
Q.1. Name two specialised tissues that provide control and coordination in multicellular organisms.
Ans. Nervous and muscular tissues.
2. Write the name and functions of any two parts of the human hind-brain.
Ans. Two parts of human hind-brain with their functions are as follows:
(i) Cerebellum: Controls & coordinates muscular movements, maintaining body posture and equilibrium. (ii) Medulla oblongata: which regulates the centre of swallowing, coughing, sneezing, salivation and vomiting.
3. Which part of the nervous system controls reflex arcs?
Ans. Spinal cord.
Q.4. How does a touch – me – not plant respond on touching? What is this movement called?
Ans. Touch – me – not plant folds its leaflets on touching. This type of movement is called Growth independent movement (nastic movement)
5. Name the sensory receptors found in the nose and on the tongue.
Ans. Olfactory receptors, gustatory receptors.
6. List two body functions that will be affected if the cerebellum gets damaged.
Ans. a. Walking in a straight line.
7. Which gland secretes growth hormone in human beings?
Ans. Pituitary gland.
SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
Q.1. Name the hormones secreted by the following endocrine glands and specify one function of each:
(a)Thyroid (b) Pituitary (c) Pancreas
Ans. a. Thyroid: Secretes Thyroxine. It regulates metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and proteins.
b. Pituitary: Secretes growth hormone. Growth hormone regulates growth and development of body.
c. Pancreas: Secretes insulin. Insulin lowers blood sugar level.
Q.2. Write one example each of the following tropic movements :
(i) Positive phototropism (ii) Negative phototropism
(iii) Positive geotropism (iv) Negative geotropism
(v) Hydrotropism (vi) Chemotropism
Ans. (i) Positive phototropism: shoots growing towards light.
(ii)Negative phototropism: roots growing away from light towards ground.
(iii) Positive geotropism: growth of roots towards earth due to the pull of the earth.
(iv)Negative geotropism: shoots growing away from the earth.
(v) Hydrotropism: roots growing towards the source of water.
(vi)Chemotropism: growth of pollen tubes towards the ovules.
Q.3. (a) An old man is advised by his doctor to take less sugar in his diet. Name the disease from which the man is suffering. Mention the hormone due to imbalance of which he is suffering from this disease. Which endocrine gland secretes this hormone?
(b) Name the endocrine gland which secretes growth hormone. What will be its effect on a person if there is: (i) Deficiency of growth hormones (ii) Excess secretion of growth hormones?
Ans. a. The man is suffering with the disease Diabetes. Insulin is the hormone which is responsible for this disease. Pancreas secretes this hormone.
b. Pituitary gland.
(i) Deficiency of growth hormone causes dwarfism. (ii) Excess secretion of growth hormone cause gigantism in a person.
Q.4. What is Chemotropism? Give one example. Name any two plant hormones and mention their functions.
Ans. Chemotropism is the movement of a part of the plant in response to a chemical stimulus. It can be positive chemotropism or negative chemotropism. Example: The growth of pollen tube towards a chemical which is produced by an ovule during the process of fertilisation in a flower.
Two plant hormones with their functions are as follows:
Auxins promote growth, cell elongation, cell differentiation, root formation.
Gibberellins stimulate stem elongation, seed germination.
Q.5. (a) Name the part of brain which controls: (i) voluntary action (ii) involuntary action.
(b) What is the significance of the peripheral nervous system? Name the components of this nervous system and distinguish between the origin of the two.
Ans.a. (i) Voluntary actions – cerebellum; (ii) Involuntary action — medulla oblongata.
b. The communication between the central nervous system and the other parts of the body is facilitated by the peripheral nervous system. Cranial nerves arise from the brain; spinal nerves arise from the spinal cord.
Q.6. How does chemical coordination occur in plants? Explain with the help of three examples.
Ans. In plants, chemical coordination occurs through various Phytohormones.
- Auxins secreted by growing tissues. They provide growth of plants.
- Gibberellins cause stem elongation, seed germination and flowering.
- Cytokinin’s present in areas of actively dividing cells like fruits, seeds. Promote cell division.
- Abscisic acid inhibits growth and respond to environmental stress.
Q. 7. Draw and label a Neuron. Explain how it carries messages.
Ans. Information from the environment is detected by dendritic tip of a neuron located in the sense organ. A chemical reaction sets off here and it creates an electrical impulse which travels from dendrite to cell body and then along the axon to its endings where it sets off the release of some chemicals. The chemicals cross the synapse and set off a similar electrical impulse in dendrites of next neuron.Another synapse at the end of its axon delivers the impulse to the other cells like muscles cells / glands (effector organs) which react to perform the action.
LONG ANSWER QUESTION
Q.1. a) Name chemical messenger of endocrine glands responsible for changes taking place in the body
b) Mention the gland which produces adrenalin and write its function
c) Name two phytohormones
Ans: a) Hormone
b) Adrenal gland
During the situation of fight or flight, secretion of this hormone causes –
- increases the blood pressure.
- increases heart beat rate.
- increases breathing rate.
- diverts blood to essential organs including the heart, brain and skeletal muscles by dilating their blood vessels and constricting those of less essential organs, such as the skin and digestive system.
c) auxin & gibberrellin
2. Give the function(s) of the following plant hormones:
a. Auxins b. Gibberellins c. Cytokinins d. Abscisic acid e. Ethylene
Ans .
- Auxins promote cell elongation, root formation, cell division, etc. It also promotes fruit growth.
- Gibberellins stimulate stem elongation, seed germination and flowering.
- Cytokinins help in breaking the dormancy of seeds and buds. They delay ageing in leaves. They also promote the opening of stomata.
- Abscisic acid promotes falling of leaves and fruits.
- Ethylene promotes ripening of fruits
Q3. Smita’s father was complaining about frequent urination, pain in legs and a frequent weight loss to Smita’s mother and she discussed the things with her daughter when Smita returned from school. Listening to this Smita told her mother that her father should go and visit a doctor immediately. The doctor diagnosed that Smita’s father was having an elevated level of blood glucose. He should take care of his diet and should exercise regularly to maintain his normal glucose level.
On the basis of the text, answer the following questions:
(i) Name the disease he is suffering from and name the hormone whose deficiency causes it.
(ii) Identify the gland that secretes it and mention the function of this hormone.
(iii) Explain how the time and amount of secretion of this hormone is regulated in human system.
Ans. (i) Disease-Diabetes, Hormone: Insulin
(ii) Gland-Pancreas: The blood glucose level is regulated by insulin hormone secreted by the pancreas.
(iii) Feedback Mechanism – Cells of pancreas secrete insulin hormone when level of blood glucose level increases in the blood. Insulin regulates the blood glucose level and its secretion gets reduced when blood glucose level falls down.
4. Mention one function for each of these hormones.
i) Thyroxine
ii) Insulin
iii) Estrogen
iv) Growth hormone
v) Testosterone.
Ans. (i) Thyroxin – Control overall metabolic rate of the body (carbohydrate, protein and fat metabolism)
(ii) Insulin – Conversion of glucose to glycogen in liver and muscles, thus decreases blood glucose level.
(iii) Estrogen – Development of female sex organ and secondary sexual characteristics like development of breast, pimples, shrill and a higher pitch voice
(iv) Growth hormone – Body growth and development of bones.
(v) Testosterone – Development of male sex organ and secondary sexual characteristics like moustache, beard & voice.
CASE STUDY QUESTION
The human brain is a 3- pound (1.4-kilogram) mass of jelly-like fats and tissues—yet it’sthe most complex of all known living structures The human brain is more complex than any other known structure in the universe. Weighing in at three pounds, on average, this spongy mass of fat and protein is made up of two overarching types of cells—called glia and neurons— and it contains many billions of each. Neurons are notable for their branch-like projections called axons and dendrites, which gather and transmit electrochemical signals. Different types of glial cells provide physical protection to neurons and help keep them, and the brain, healthy. Together, this complex network of cells gives rise to every aspect of our shared humanity. We could not breathe, play, love, or remember without the brain.
Answer
1)Animals such as elephants, dolphins, and whales actually have larger brains, but humans have the most developed cerebrum. It’s packed to capacity inside our skulls and is highly folded. Why our brain is highly folded?
To increase the surface area of the brain to receive sensory impulses from various receptors, interpret the sensory information with the information that is stored in the brain and respond accordingly
2)Which among this is not a function of cerebrum?
c) Posture
3)Which among these protects our brain?
a)Neurotransmitter b) Cerebrospinal fluid c)Meninges d) Grey matter
ii) b & c
2 All the living organisms (plants and animals) respond and react to changes in the environment around them. The changes in the environment to which the organisms respond and react are called stimuli (singular: stimulus). The living organisms show response to stimuli such as light, heat, cold, sound, smell, taste, touch, pressure, pain, water, and force of gravity, etc. The response of organisms to a stimulus is usually in the form of some movement of their body parts. For example, if a man touches a very hot utensil accidently, he quickly pulls his hand away from the hot utensil. Here, heat is the stimulus and the man reacts by moving his hand away from the hot utensil. Similarly, when the Sun is bright, we close our eyes. In this case, light is the stimulus and we react by closing the eyes.
Answer
1. Humans respond to changes in their surrounding environment. The changes are known as _
b. stimuli
2. You close your eyes when your friend point the torchlight towards your eye. Which sensory organ is involved?
b. Eyes
3. A baby cries when hears the thunder. What is the stimulus that is involved?
a. sound
4. Based on the situation below, which situation shown human respond to stimuli?
I- A boy pulls his hand when touching a hot object.
II- A girl is reading a book.
III- A girl closes her ear when hearing the thunder.
IV- A boy is walking to school.
c. I and III
5. A response is ____
c. A reaction to a change in the environment
Biology is one of the natural sciences which involves the study of humans, plants and other living organisms, their structure, growth, function, evolution and so on under various specializations such as botany, zoology, molecular biology, microbiology, genetics, marine biology etc.
Students can pursue the subject at senior secondary and university level to have amazing careers in the field of Biology. To score well in these topics, refer to the important questions and answers from the chapter along with other prescribes materials.
All the best!
#CBSE #Class #Biology #Control #Coordination #Important #Questions #Answers