Jagran Josh
CBSE Class 10 Physics Human Eye Important Questions and Answers: With the help of the important questions and answers to the chapter Human Eye and Colourful World, students in CBSE Class 10 can achieve their dream scores in the Science board examination. These questions have been listed along with the best answers by subject experts so that students are well prepared with all major questions that can be asked in CBSE Class 10 Science board examination 2022-23.
Human Eye and Colourful World chapter appears as Chapter 11 in the NCERT textbooks. However, according to the latest rationalised CBSE Class 10 syllabus 2022-23, it is now chapter 10 in the syllabus. In the previous chapter Light: Reflection and Refraction, topics such as refraction of light by Lenses and nature, position and relative size of images formed by lenses. Since the human eye uses light and has a lens in its structure that enables us to see objects, Chapter 10 Human Eye and Colourful World focuses on the human eye, its various functions and some of the optical phenomena in nature.
CBSE Class 10 Important Questions on Science Chapter- Human Eye and Colourful World
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
1. Colour of sky appears blue, due to the
(A) atmospheric refraction
(B) presence of plants in water
(C) scattering of light
(D) none of these
2. Twinkling of stars is due to
(a) Reflection of light by clouds
(b) scattering of light by dust particles
(c) dispersion of light by water drops
(d) atmospheric refraction of starlight
3. Red colour is used as danger sign as
(A) red colour scattered least by smoke
(B) red colour scattered most by smoke
(C) Red colour absorbs by the smoke
(D) red colour moves fast in air
4. The scattering of light by colloidal particles is called
(a) Tyndall effect
(b) dispersion
(c) atmospheric refraction
(d) internal reflection
5. Which colour of light refracts most when passes through a prism-
(A) yellow
(B) Red
(C) orange
(D) indigo
6. Which of the following controls the amount of light entering the eye
(A) pupil
(B) iris
(C) cornea
(D) lens
7. When white light passes through a prism, the component colour which Undergoes maximum bending is
(a) red
(b) green
(c) violet
(d) blue
8. The change of focal length of eye lens is caused by the action of the
(A) ciliary muscles
(B) iris
(C) cornea
(D) pupil
9. Sunlight is passed through a transparent medium having very fine particles These particles scatter light.Which among the given components of light undergoes more scattering?
(a) red
(b) orange
(c) yellow
(d) blue
10 The least distance of distinct vision for a young adult with normal vision is about
(a) 25 m
(b) 2.5 cm
(c) 25 cm
(d) 2.5 m
ASSERTION AND REASON BASED QUESTIONS
Instructions: A statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is
given.Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
(A) Both Assertion and Reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(B) Both Assertion and Reason are true and the reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(C) Assertion is true but the Reason is false.
(D) Assertion is false but Reason is true.
1. Assertion:A rainbow is a natural spectrum appearing in the sky after a
Rain Shower.
Reason- A rainbow is always formed in a direction opposite to that of theSun.
2. Assertion- myopia is called far-slightness
Reason- myopia is corrected by using a concave lens in front of eye lens
3. Assertion: When a beam of light strike fine particles of smoke, the path of the beam becomes visible.
Reason :Fine particles of smoke scatter light.
4. Assertion: White light is dispersed into its seven-colour components by a prism.
Reason : Different colours of light bend through different angles with respect tothe incident ray, as they pass through a prism.
5. Assertion: The stars twinkle, while the planets do not.
Reason: The stars are much bigger in size than the planets.
6. Assertion- cataract can be corrected by using bi-focal lens.
Reason – The crystalline lens of old peoples become milky and cloudy; this is due to the age of person.
7. Assertion- atmospheric refraction is responsible for advance sunrise and delayed sunset.
Reason- This is happening due to the temperature difference between the layers of air.
CASE STUDY BASED QUESTIONS
- One of nature’s most splendid masterpieces is the rainbow. A rainbow is an excellent demonstration of the dispersion of light and one more piece of evidence that visible light is composed of a spectrum of wavelengths, each associated with a distinct colour. To view a rainbow, the sun must be at your back as you look at an approximately 40 degree angle above the ground into a region of the atmosphere with suspended droplets of water or even a light mist. Each individual droplet of water acts as a tiny prism that both disperses the light and reflects it back to your eye.
i) Formation of rainbow involves some natural phenomena which are in the correct order respectively is
a)refraction, dispersion, internal reflection and refraction
b)refraction, dispersion, internal reflection
c)reflection, refraction ,dispersion and refraction
d) dispersion , reflection, refraction and internal reflection
ii) During the formation of a rainbow the position of observer and sun is
a) Observer behind sun
b) sun behind the observer
b) Observer facing sun
d) at any position
iii) During the formation of rainbow, dispersion of sunlight is done by
a) tiny air molecules
b) dust particles of atmosphere
c) tiny droplets of rain water suspended in air
d) air and water
iv)The dispersion of light into its components by prism is due to
a) each component get deviated by the same angle by refraction
b) each component gets deviated by a different angle by refraction
c)reflection of each component light by different angle
d)reflection of each component light by same angle
- When a ray of light incident on a prism it will split in seven colours that is called dispersion of light. A prism is a transparent refracting body bounded by plane faces which are inclined to each other at a particular angle called angle of prism.. When a ray of light passes through a prism, it suffers refraction twice and hence the ray deviates through a certain angle from its original path. The angle between the incident ray and emergent ray is called angle of deviation.
i. For which colour the angle of deviation is minimum?
a Red
b Blue
c Violet
d Yellow
ii When a white light falls on a prism, the ray at its surface suffers:
(A) Refraction only
(B) dispersion only
(C) deviation only
(D) all of above
iii In nature, dispersion of light is happening in
(A) Blue colour of sky
(B) Formation of rainbow
(C) Twinkling of stars
(D) advance sunrise
iv The cause of dispersion of light is –
(A) All colours of light travel with the speed more than the speed of light
(B) All colours have different angle of deviation
(C) All the colours of light do not travel with same speed
(D) All the colours have same wavelength
VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
1. What is meant by the power of accommodation of the eye ?
2. When a monochromatic light having only one wavelength, passes through a prism, will it show dispersion?
3. Name the component of white light that deviates the least while passing through a glass prism.
4. A student has difficulty reading the blackboard while sitting in the last row. What could be the defect the child is suffering from ? How can it be corrected?
5. A student has difficulty reading the blackboard while sitting in the front row. What could be the defect the child is suffering from ? How can it be corrected?
6. A person with a myopic eye cannot see objects beyond 1.2 m distinctly. What should be the type of the corrective lens used to restore proper vision ?
7. Name the component of white light that deviates the most while passing through a glass prism.
8. What is the far point and near point of the human eye with normal vision ?
SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
1. What is colour-blindness? What kind of retinal cells are lacking in a person suffering from this defect?
2. What happens to the image distance in the eye when we increase the distance of an object from the eye ?
3. Explain why the planets do not twinkle?
4. Why is a normal eye not able to see clearly the objects placed closer than 25 cm?
5. Why do stars twinkle?
6. Why does the sky appear dark instead of blue to an astronaut?
7. Why does the sun appear reddish early in the morning?
LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. State the reason behind the following phenomenon/observation:
A. Rainbow formation
B. Reddening of sun’s disc in the early morning and late evening
C. Flattening of sun’s disc at sunrise and sunset
D. Pathway of light visible in a foggy atmosphere or a dusty room/smoke filled room
2 . How can we see objects?
3. The far point of a myopic person is 80 cm in front of the eye. What is the nature and power of the lens required to correct the problem?
4. Draw the sketch diagram of the human eye. And explain about the different parts of the eye.
Answers to the important Questions on Science Chapter- Human Eye and Colourful World
|
S No |
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS |
|
1 |
C |
|
2 |
D |
|
3 |
A |
|
4 |
A |
|
5 |
D |
|
6 |
B |
|
7 |
C |
|
8 |
A |
|
9 |
D |
|
10 |
C |
|
S No |
ASSERTION AND REASON QUESTIONS |
|
1 |
B |
|
2 |
D |
|
3 |
A |
|
4 |
A |
|
5 |
C |
|
6 |
D |
|
S No |
CASE STUDY QUESTIONS |
|
1 i |
A |
|
ii |
B |
|
iii |
C |
|
Iv |
B |
|
2 i |
A |
|
ii |
D |
|
iii |
B |
|
iv |
C |
VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
1. What is meant by the power of accommodation of the eye ?
Answer: The power of accommodation of the eye is the maximum variation of its power for focusing on near and far (distant) objects.
2. When a monochromatic light having only one wavelength, passes through a prism, will it show dispersion?
Answer: No, it will not show dispersion. It will only show deviation.
3. Name the component of white light that deviates the least while passing through a glass prism.
Answer: Least deviated component: Red
4. A student has difficulty reading the blackboard while sitting in the last row. What could be the defect the child is suffering from ? How can it be corrected?
Answer: The child is suffering from myopia. The child should use concave lens of suitable focal length.
5. A student has difficulty reading the blackboard while sitting in the front row. What could be the defect the child is suffering from ? How can it be corrected?
Answer: The child is suffering from hypermetropia. The child should use convex lens of suitable focal length.
6. A person with a myopic eye cannot see objects beyond 1.2 m distinctly. What should be the type of the corrective lens used to restore proper vision ?
Answer: Concave lens.
7. Name the component of white light that deviates the most while passing through a glass prism.
Answer: Most deviated component: Violet
8. What is the far point and near point of the human eye with normal vision ?
Answer: For a human eye with normal vision the far point is at infinity and the near point is 25 cm from the eye.
SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
1. What is colour-blindness? What kind of retinal cells are lacking in a person suffering from this defect?
Answer: The defect of the eye due to which a person is unable to distinguish between certain colours, is known as colour blindness. Cone-shaped retinal cells are responsible for making a person differentiate between colours. The colour blindpersons do not possess cone cells that respond to certain colours.
2. What happens to the image distance in the eye when we increase the distance of an object from the eye ?
Answer: The eye lens of a normal eye forms the images of objects at various distances on the same retina. Therefore, the image distance in the eye remains the same.
3. Explain why the planets do not twinkle?
Answer: The planets are much nearer to the earth than stars and because of this they can be considered as large source of light. If a planet is considered to be a collection of a very large number of point sources of light, then the average value of change in the amount of light entering the eye from all point size light sources is zero. Due to this the effect of twinkling is nullified.
4. Why is a normal eye not able to see clearly the objects placed closer than 25 cm?
Ans: A normal eye is unable to clearly see objects placed closer than 25 cm because the ciliary muscles of eyes are unable to contract beyond a certain limit. If the object is placed at a distance less than 25 cm from the eye, then the object appears blurred and produces strain in the eyes.
5. Why do stars twinkle?
Answer: Stars appear to twinkle due to atmospheric refraction. The light of a star after the entry of light in earth’s atmosphere undergoes refraction continuously till it reaches the surface of the earth. Stars are far away. So, they are the point source of light. As the path of light coming from stars keeps changing, thus the apparent position of stars keeps changing and the amount of light from stars entering the eye keeps twinkling. Due to which a star sometimes appears bright and sometimes dim, which is the effect of twinkling.
6. Why does the sky appear dark instead of blue to an astronaut?
Answer: As an astronaut moves away from the atmosphere of earth, the atmosphere becomes thin. Due to the absence of molecules (or dust particles) in air, the scattering of light does not take place. Thus, the sky appears dark in the absence of scattering.
7. Why does the sun appear reddish early in the morning?
Answer: The light coming from the sun passes through various denser layers of air in the earth’s atmosphere before reaching our eyes near the horizon. Most of the part of blue light and light of small wavelength gets scattered by dust particles near the horizon. So, the light reaching our eyes is of large wavelength. Due to this the sun appears reddish at the time of sunrise and sunset.
LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. State the reason behind the following phenomenon/observation:
- Rainbow formation
- Reddening of sun’s disc in the early morning and late evening
- Flattening of sun’s disc at sunrise and sunset
- Pathway of light visible in a foggy atmosphere or a dusty room/smoke filled room
Answer: A. Light when enters tiny raindrops in the atmosphere, undergoes Refraction,dispersion,internal reflection,again refraction
B. Scattering away of smaller wavelength of light by particles of atmosphere
C. Atmospheric refraction
D. Tyndall effect/scattering of light
2 . How can we see objects?
Answer: – First light enters in our eye from cornea. If the light is very bright, the iris contracts the pupil to allow less light to enter the eye and in dim light the iris expends pupil to allow more light in the eye. This light incident on the eye lens and image is formed at the retina. The optic nerves transmit electrical impulses to the brain and we get information about the object.
3. The far point of a myopic person is 80 cm in front of the eye. What is thenature and power of the lens required to correct the problem?
Answer: The person is suffering from an eye defect called myopia. In this defect, the image is formed in front of the retina.
Hence, a concave lens is used to correct this defect of vision.
Object distance, u = infinity
Image distance, v = −80 cm
Focal length = f
According to the lens formula, 1/v-1/u=1/f
1/-80 -1/α =1/f
1/f=1/-80
f= -0.8m
P= 1/f= 1/-0.8 =-1.25D
A concave lens of power −1.25 D is required by the person to correct his defect.
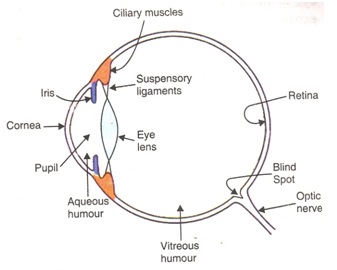
4. Draw the sketch diagram of the human eye. And explain about the different parts of the eye.
Answer: The human eye is the most sensitive part of the human body. By closing our eyes, we can sense some objects with their smell, taste, sound they make or by touching them but we cannot identify the colour without opening our eyes.
Parts of human eyes: –
Cornea- the outermost part of the eye, light enters from this part.
Eye lens- it is a convex lens its curvature is controlled by ciliary muscles.
Iris- The part of the eye which controls the size of the pupil.
Pupil- The aperture of the pupil varies with the help of the iris. Pupil regulates and controls the amount of light entering the eye.
Retina- The light-sensitive screen, where the image of any object is formed
These were some CBSE Class 10 Physics Human Eye Important Questions and Answers which students of CBSE Class 10 Science Board Examination 2023 should be well versed with.
All the best!
#CBSE #Class #Physics #Human #Eye #Important #Questions #Answers