Jagran Josh
Class 12 Biology Revision Notes 2023-24: Check CBSE Class 12 Biology short notes, revision notes, CBSE notes and NEET important notes for quick and effective revision. Get chapter-wise revision notes from subject matter experts.

Download CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 6 Evolution Revision Notes PDF
Evolution CBSE Notes: The education system of contemporary India was very different from what we experience today. The growth of education is phenomenal and exciting to know about. Earlier, there used to be no notebooks to make notes and keep things for the future. Whatever was explained in the class was supposed to be remembered by the students. That education system was teacher-centred, as most things depended on and were done according to teachers. But no worries; you are enjoying the modern education system of India, which is much more advanced and student-centred. Now the education board places emphasis on the holistic development of the students. There are study materials available online and offline from which students can benefit.
Here, we are going to provide you with the short notes for CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 6. This chapter is on Evolution. These notes can be used as revision notes at the time of exams or teaching notes for quickly revising the content of the chapter. These notes include text and diagrams that are taken from the revised NCERT Class 12 Biology textbook for better understanding. Now you can go ahead and read Chapter 6 Evolution revision notes of CBSE Class 12 Biology. The free, downloadable PDF of this content is attached at the tail of this article.
CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 6 Revision Notes
Introduction to Evolution:
- It is the process of gradual change that occurs in a species over time creating new species from a common ancestor.
- The concept of evolution helps explain the biodiversity and complexity of life on Earth.
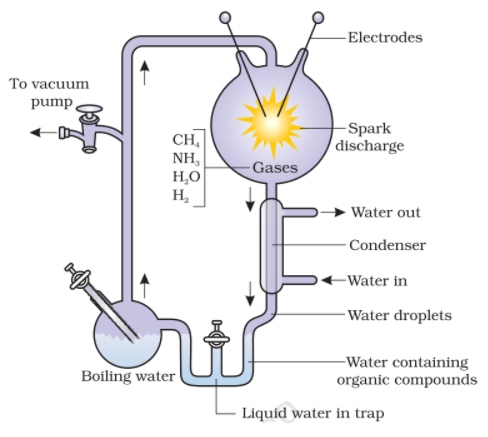
Miller-Urey Experiment
Theories of Evolution:
Lamarck’s Theory:
- Proposed by Jean-Baptiste Lamarck.
- Suggested the theory of inheritance of acquired characteristics. It is also called theory of use and disuse.
- According to this theory, traits acquired during an organism’s lifetime could be passed on to its offspring.
- Example: The elongated neck of giraffes, acquired by stretching to reach leaves, would be passed on to future generations.
Darwin’s Theory:
- Charles Darwin proposed the theory of Natural Selection.
- Natural Selection states that organisms which are able to adapt themselves to the surrounding environment are supported in their survival.
- It was also described as the “Survival of the fittest.”
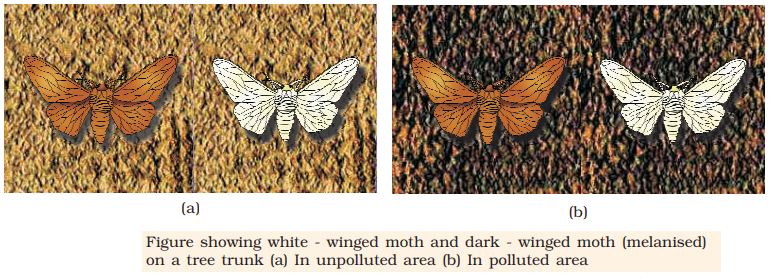
Evidence of Evolution:
Fossil Records:
- Fossils are the remains of living beings that existed in the past and whose remains can be found in sedimentary rocks.
- These are the evidence of extinct species and transitional forms that link different groups of organisms.
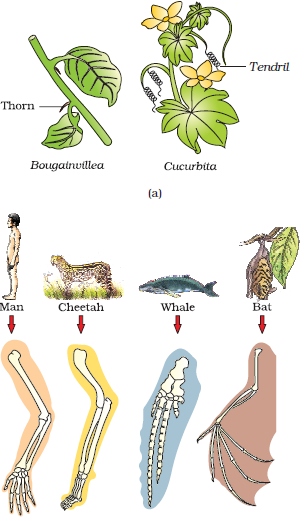
Comparative Anatomy:
- Comparative anatomy involves the study of similarities and differences between the anatomical or morphological features of different species.
- Homologous structures: similar in structure but may have different functions, suggesting a common evolutionary origin. Eg: forelimbs of humans and bats.
- Analogous structures: perform similar functions but have different evolutionary origins. Eg: Wings of birds and butterflies.
Embryological Evidence:
- The study of embryo development reveals similarities among different organisms, suggesting common ancestry.
- Embryos of diverse organisms may display similar stages or structures during development.
Speciation:
- Speciation is the process by which one species splits into two or more distinct species.
- It can occur through allopatric (also called geographical isolation) or sympatric (also called reproductive isolation) mechanisms.
Hardy-Weinberg Principle
According to the NCERT textbook “In a given population one can find out the frequency of occurrence of alleles of a gene or a locus. This frequency is supposed to remain fixed and even remain the same through generations. Hardy-Weinberg’s principle stated it using algebraic equations. This principle says that allele frequencies in a population are stable and is constant from generation to generation. The gene pool (total genes and their alleles in a population) remains constant. This is called genetic equilibrium.” The total of all allele frequencies in a population is 1.
Hardy-Weinberg equation: p2+2pq+q2=1
Factors to Affect Hardy-Weinberg Principle
- Gene Flow: The transfer of genetic information from one population to another is called gene flow. It is also called gene migration,
- Genetic Drift: The change in gene frequency of an existing gene variant in the population due to a sudden change.
- Mutation: Change in the normal sequence of nucleic acid ( DNA and RNA).
- Genetic Recombination: Rearrangement of the sequence of DNA after breaking and rejoining of chromosomes.
- Natural Selection: Mechanism by which fittest organisms are favoured for their survival.
Read:
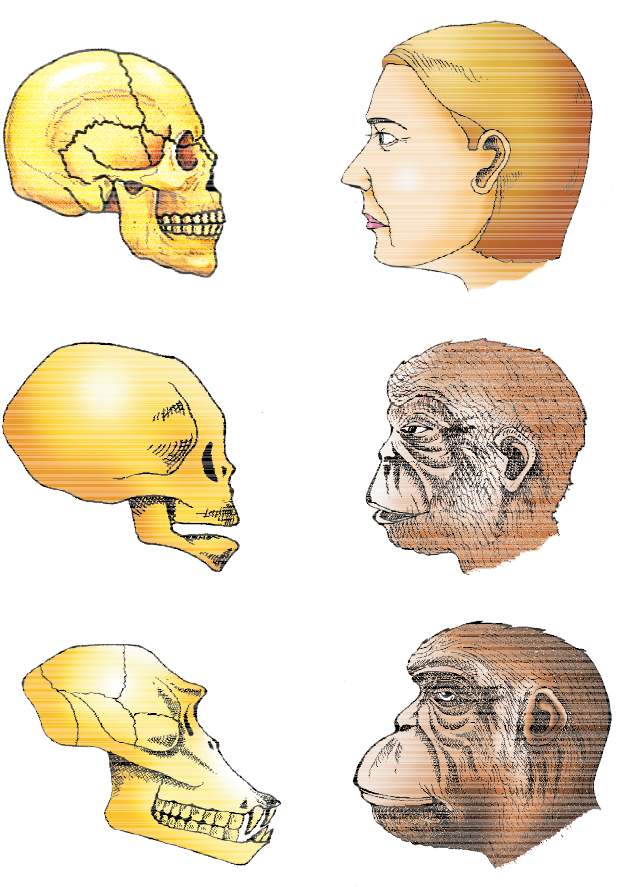
Human Evolution:
|
15 mya |
Dryopithecus and Ramapithecus |
|
|
2 mya |
Australopithecines |
Probably lived in East African grasslands |
|
Homo habilis |
650-800cc brain capacity |
|
|
1.5 mya |
Homo erectus |
900cc brain capacity |
|
1,00,000-40,000 years back |
Neanderthal man |
1400cc brain capacity |
|
75,000-10,000 years ago |
Homo sapiens |
Pre-historic cave art developed about 18,000 years ago |
Read: NCERT Class 12 Biology Revision Notes Chapter-Wise
Related:
#CBSE #Class #Biology #Evolution #Revision #Notes #Download #PDF

