Jagran Josh
Class 12 Chemistry Chemical Kinetics MCQs: MCQs for Class 12 Chemical Kinetics chapter are prepared as per the revised CBSE syllabus and are important for CBSE Board Exam 2024. Download all questions and answers in PDF here.
Class 12 Chemical Kinetics MCQs: Students of CBSE Class 12 often get stressed by the hype around the board exams, however, if they have prepared for the exams in the right way then there’s nothing to worry about it. Students must be aware of the exam pattern and the questions’ format that is to be followed for the final exams. Now, as per the latest exam pattern, the CBSE board exams are going to offer the students a variety of questions including MCQs, case-studies, assertion-reasoning questions, etc. Thus, students must have hands on experience in solving all such questions with accuracy.
Jagran Josh is dedicated to bringing you reliable study material with the help of which you can get exam ready and increase your chances of scoring high in CBSE Board Exams. This article is about the Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter Chemical Kinetics. You will get here the questions prepared by subject experts which are completely based on the revised CBSE syllabus. All the questions are important from the exam point of view. Check all the MCQs with answers for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 3 – Chemical Kinetics below and download the same from the link provided towards the end.
Also Check: CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Syllabus 2023-24
MCQs for CBSE Class 12 Chemical Kinetics (Chemistry) 2023-24
1.The term – dx/dt in a rate equation refers to :
(a) the conc. of a reactant
(b) the decrease in conc. of the reactant with time
(c) the velocity constant of reaction
(d) None of these
Answer: (b) the decrease in conc. of the reactant with time
2.For a reaction P + Q → 2 R + S , the incorrect statement is
(a) Rate of disappearance of P = Rate of appearance of S
(b) Rate of disappearance of Q = 2 x Rate of appearance of R
(c) Rate of disappearance of Q = Rate of disappearance of P
(d) Rate of disappearance of Q = 1⁄2 x Rate of appearance of R
Answer: (b) Rate of disappearance of Q = 2 x Rate of appearance of R
3.In a reaction, 2X → Y, the concentration of X decreases from 0.50 M to 0.38 M in 10 min. Whatis the rate of reaction in Ms-1 during this interval?
(a) 2 × 10-4
(b) 4 × 10-2
(c) 2 × 10-2
(d) 1 × 10-2
Answer: (a) 2 × 10-4
4.Instantaneous rate of a chemical reaction is
(a) rate of reaction in the beginning
(b) rate of reaction at the end
(c) rate of reaction at a given instant
(d) rate of reaction between two specific time intervals
Answer: (c) rate of reaction at a given instant
5.A first order reaction has a rate constant 1.15 × 10-3s-1. Time taken for 5 g of this reactant to reduce to 3 g is
(a) 444 s
(b) 400 s
(c) 528 s
(d) 669 s
Answer: (a) 444 s
6.For the reaction A + 2B → C, rate is given by R = [A] [B]2 then the order of the reaction is
(a) 3
(b) 6
(c) 5
(d) 7
Answer: (a) 3
7.Order of reaction is decided by
(a) temperature
(b) mechanism of reaction as well as relative concentration of reactants
(c) molecularity
(d) pressure
Answer: (b) mechanism of reaction as well as relative concentration of reactants
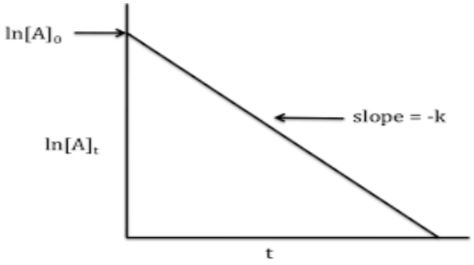
8.A plot is shown below between concentration and time t. Which of the given orders is indicated by the graph
(a) Zero Order
(b) Second Order
(c) First Order
(d) Fractional Order
Answer: (c) First Order
9.A zero order reaction is one whose rate is independent of
(a) the concentration of the reactants
(b) the temperature of reaction
(c) the concentration of the product
(d) the material of the vessel in which reaction is carried out
Answer: (a) the concentration of the reactants
10.A catalyst increases the reaction rate by:
(a) decreasing enthalpy
(b) increasing internal energy
(c) decreasing activation enthalpy
(d) increasing activation enthalpy
Answer: (c) decreasing activation enthalpy
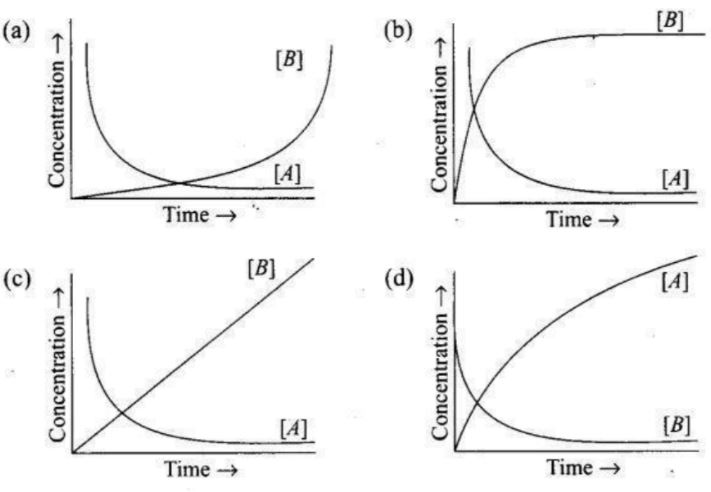
11.Consider the reaction A —> B. The concentration of both the reactants and the products varies exponentially with time. Which of the following figures correctly describes the change in concentration of reactants and products with time?
Answer: (b)
12.A first order reaction takes 40 min for 30% decomposition. t1/2 will be
(a) 77.7 min
(b) 52.5 min
(c) 46.2 min
(d) 22.7 min
Answer: (a) 77.7 min
13.In a reaction, the threshold energy is equal to
(a) activation energy + normal energy of reactants
(b) activation energy – normal energy of reactants
(c) normal energy of reactants – activation energy
(d) average kinetic energy of molecules of reactants
Answer: (a) activation energy + normal energy of reactants
14.Which of the following influences the reaction rate performed in a solution?
(a) Temperature
(b) Activation energy
(c) Catalyst
(d) All of the above
Answer: (d) All of the above
15.Compounds A and B react according to the following chemical equation.
A(g)+2B(g)→2C(g) Concentration of either ‘A’ or ‘B ’ were changed keeping the concentrations of one of the reactantsconstant and rates were measured as a function of initial concentration. Following results were obtained. Choose the correct option for the rate equations for this reaction.
|
Expt |
[A] |
[B] |
Initial Rate (mol L-1s–1) |
|
I |
0.01 |
0.01 |
0.005 |
|
II |
0.02 |
0.01 |
0.020 |
|
III |
0.02 |
0.03 |
0.060 |
(a) Rate = k[A] [B]
(b) Rate = k[A]1[B]2
(c) Rate = k[A]2[B]2
(d) Rate = k[A]2[B]
Answer: (d) Rate = k[A]2[B]
|
Download CBSE Class 12 Chemistry MCQs for Chemical Kinetics in PDF (Link to be updated) |
Also Read|
#CBSE #Class #Chemistry #MCQs #Chapter #Chemical #Kinetics #Download #PDF #Quick #Revision