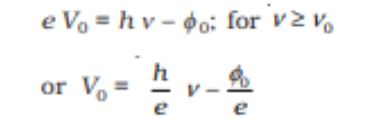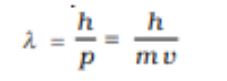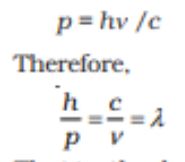Jagran Josh
Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Formulas & Diagrams: Students can find a list of important definitions, diagrams, and formulas for CBSE Class 12 Physics Chapter 11, Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter.
CBSE Class 12 Physics Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Formula list: Physics is a subject filled with lots of formulas and definitions for students to remember. It also consists of diagrams, graphs, and important standard values that have to be understood and mugged up at times. To avoid any confusion and ensure that students don’t miss out on any important formula, definition, graph, diagram, or standard value, we have brought a formula sheet along with important definitions and diagrams for students.
Here, students can find the formula sheet for CBSE Class 12 Physics Chapter 11, Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter. It is an important chapter from the CBSE Board Exam’s point of view. Several numerical, definitions, diagrams, and theories can be asked from the chapter in the examinations. The dual nature of Radiation and Matter is a kind of chapter that is filled with practical concepts, experiments, and important theories. So, the entire chapter has to be read thoroughly before you start solving numerical problems. Students will also have to learn certain symbols, their formulas, and some standard values in order to be able to solve the numerical.
We understand that it becomes difficult for students to keep looking for values, formulas, and graphs while solving exercise questions and preparing for examinations. Thus, to assist you in your preparation journey, we have brought the formula sheet for you. Students can find all the important topics from CBSE Class 12 Physics Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter, here.
Related:
Standard Values:
Speed of light- 3 x 108 m/s
E/m = 1.76 × 1011 C/kg
1 eV = 1.602 ×10 –19 J
Formulas:
Maximum Kinetic Energy (Kmax)= eVo
Einstien’s Photoelectric Equation= Maximum Kinetic Energy (In terms of quantum of energy)=
Threshold Frequency =
Photoelectric Equation=
Energy= hv
Momentum=
De Brogile Relation= Wavelength=
De Brogile Wavelength of a photon=
Definitions:
- Thermionic emission: By suitably heating, sufficient thermal energy can be imparted to the free electrons to enable them to come out of the metal
- Field emission: By applying a very strong electric field (of the order of 108 V m–1) to a metal, electrons can be pulled out of the metal, as in a spark plug
- Photoelectric emission: When light of suitable frequency illuminates a metal surface, electrons are emitted from the metal surface. These photo(light)-generated electrons are called photoelectrons.
- Photoelectric effect Hertz Observations– In his photoelectric experiment, Hertz observed that high voltage sparks across the detector loop were enhanced when the emitter plate was illuminated by ultraviolet light from an arc lamp. Light shining on the metal surface somehow facilitated the escape of free, charged particles which we now know as electrons. When light falls on a metal surface, some electrons near the surface absorb enough energy from the incident radiation to overcome the attraction of the positive ions in the material of the surface. After gaining sufficient energy from the incident light, the electrons escape from the surface of the metal into the surrounding space.
- Hallwach’s and Lenard’s observations– Lenard (1862-1947) observed that when ultraviolet radiations were allowed to fall on the emitter plate of an evacuated glass tube enclosing two electrodes (metal plates), current flows in the circuit. As soon as the ultraviolet radiations were stopped, the current flow also stopped. These observations indicate that when ultraviolet radiations fall on the emitter plate C, electrons are ejected from it which are attracted towards the positive, collector plate A by the electric field. a negatively charged zinc plate to an electroscope. He observed that the zinc plate lost its charge when it was illuminated by ultraviolet light. Further, the uncharged zinc plate became positively charged when it was irradiated by ultraviolet light. The positive charge on a positively charged zinc plate was found to be further enhanced when it was illuminated by ultraviolet light.
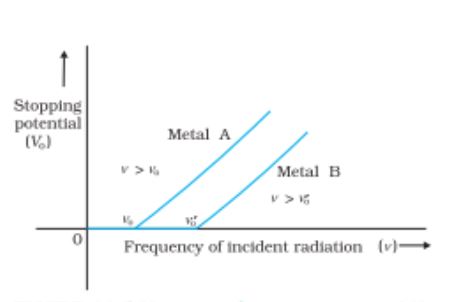
- Threshold Frequency– when the frequency of the incident light is smaller than a certain minimum value, it is called the threshold frequency.
- Photoelectric effect- All the photosensitive substances emit electrons when they are illuminated by light, this phenomenon is called the photoelectric effect.
- Photo electrons– The electrons emitted during the photoelectric effect are named as photoelectrons.
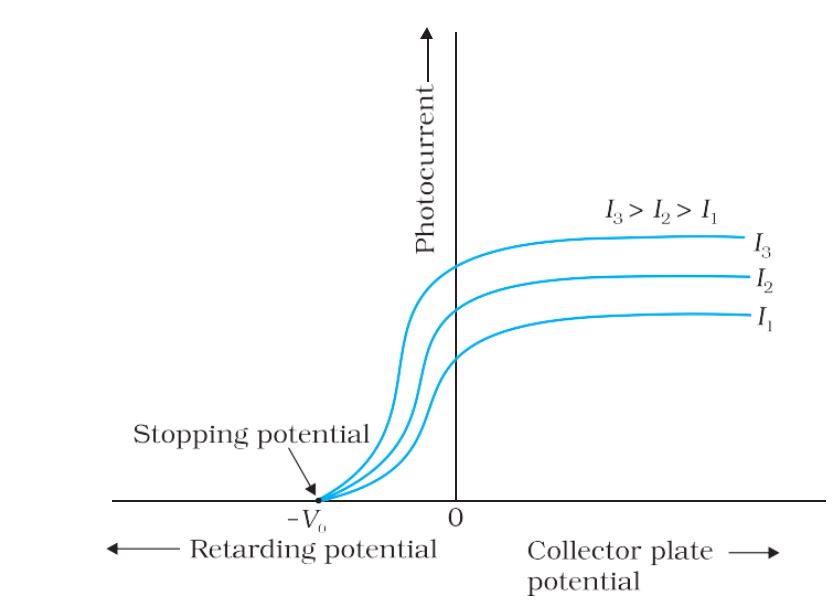
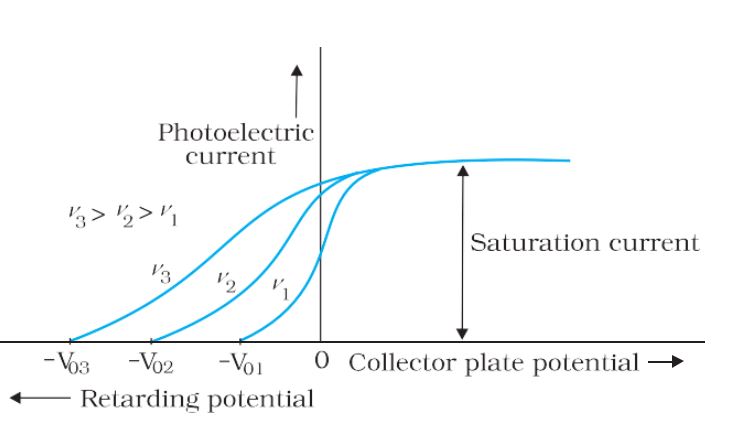
- Stopping Potential– For a particular frequency of incident radiation, the minimum negative (retarding) potential V0 given to plate A for which the photocurrent stops or becomes zero is called the cutoff or stopping potential.
- Saturation Current– The maximum value of the photoelectric current is called saturation current.
Diagrams:
Experimental study of the photoelectric effect
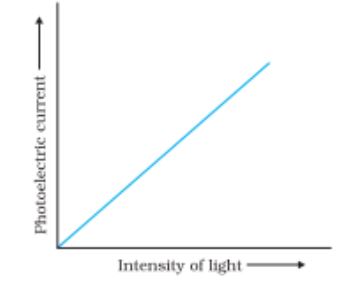
Variation of photoelectric current with intensity of light
Variation of photocurrent with different intensity of incident radiation
Variation of photocurrent with different frequencies of incident radiation
Variation of stopping potential with frequency of incident radiation
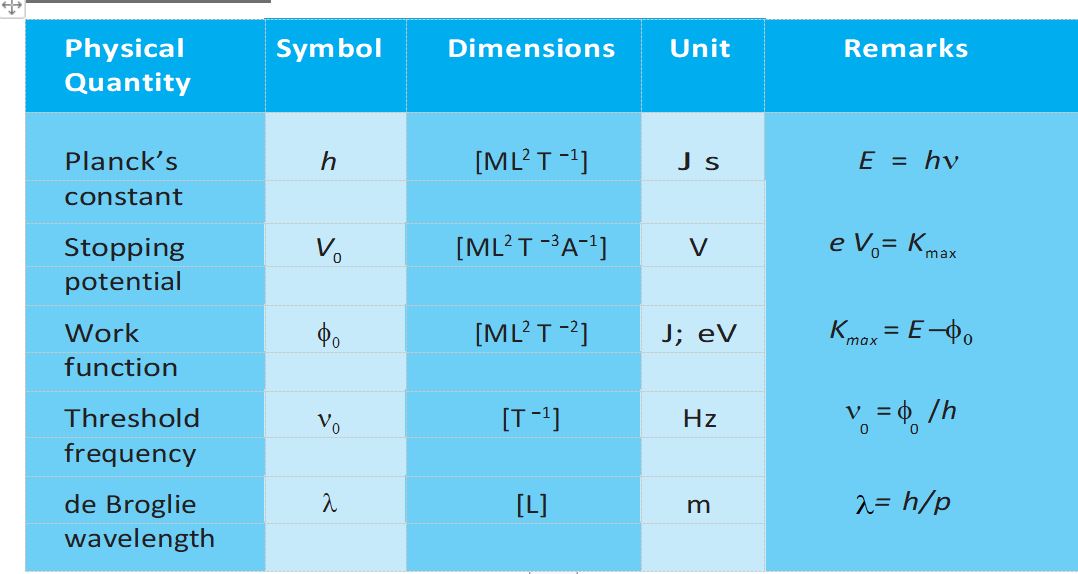
Important Physical Quantities along with their symbols and units
To download the formula sheet in PDF, click on the link below
#CBSE #Class #Physics #Dual #Nature #Radiation #Matter #Formula #List #Definitions #Diagrams