Jagran Josh
Ray Optics and Optical Instruments Formulas & Ray Diagrams: Students can find a list of important ray diagrams and formulas for CBSE Class 12 Physics Chapter 9, Ray Optics and Optical Instruments.
CBSE Class 12 Physics Ray Optics Formula list: Ray Optics is an important chapter for CBSE Class 12 students. Usually, four marker questions from the chapter are asked in the CBSE Board Examinations. Derivations, formulas, ray diagrams, and important concepts from ray optics and optical instruments are vital for scoring high marks in Class 12 Physics.
We understand that it is difficult for students to keep looking for formulas and ray diagrams all around the chapter while solving NCERT questions or practicing NCERT Solutions. So, we have provided here a complete list of formulas and ray diagrams for CBSE Class 12 Physics Chapter 9, Ray Optics and Optical Instruments. A PDF download link has also been attached below for future reference.
It is equally important for students to keep a formula list handy during examinations, to quickly memorize the important formulas required for solving numerical. Also, for this chapter, ray diagrams are essential because these can be directly asked in the CBSE Board Examinations. Thus, students must have a look at the list presented below and they should also download the PDF to keep it ready for future use.
Related:
CBSE Class 12 Physics Syllabus 2023-2024
CBSE Class 12 Physics Deleted Syllabus 2023-2024
CBSE Class 12 Physics Sample Paper 2023-2024
CBSE Class 12 Physics Chapter 9, Ray Optics and Optical Instruments Formula List is presented below:
Formulas:
Focal Length (f) = R/2
Mirror Equation= 1/v + 1/u = 1f
Linear Magnification (m) = height of the image/ height of the object
= h’/ h
Magnification Formula = – v/u
Snell’s law of refraction/Refractive Index= sin i/sin r
Apparent depth = Real depth/ Refractive Index of the medium
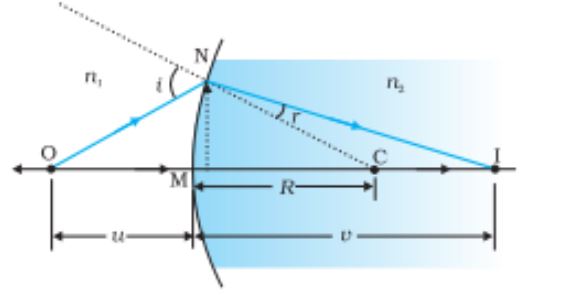
Relation between object and image distance = [n2/v – n1/u]= (n2-n1)/R
Lens Maker’s Formula =
Power of lens (P)= 1/f
Total magnification= product of multiple magnifications (m1 x m2 x m3….)
Total power of lens (P)= P1 + P2 + P3+ …….
Minimum Deviation = (n 21- 1)/A
Magnification in simple microscope (m) = 1+ D/f
Total Magnification = Mo x Me
= [ (L/fo) x (D/fe) ]
Length of telescope tube = fo + fe
Magnification of telescope = fo/fe
CBSE Class 12 Physics Chapter 9, Ray Optics and Optical Instruments Ray Diagrams are presented below:
Ray Diagrams
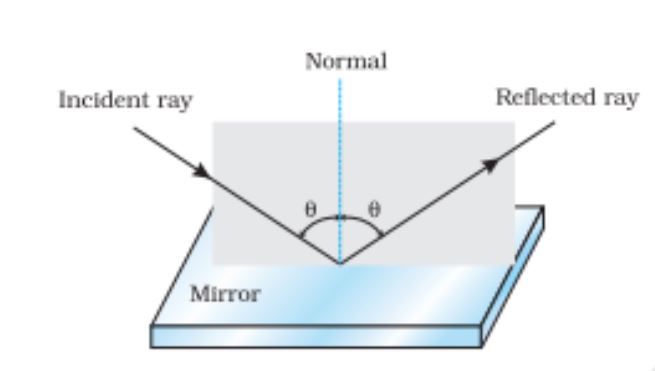
Reflection of light by spherical mirrors
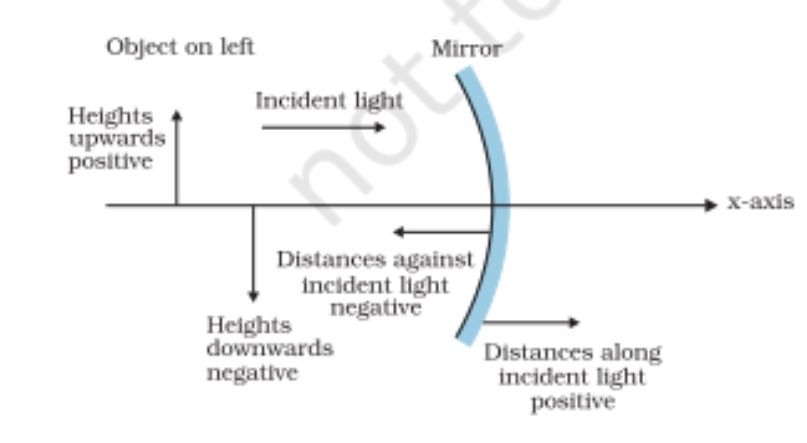
Sign Convention
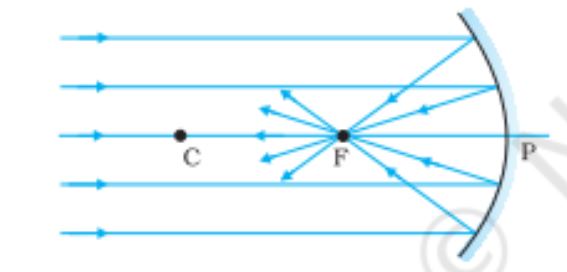
Concave mirror when rays are paraxial
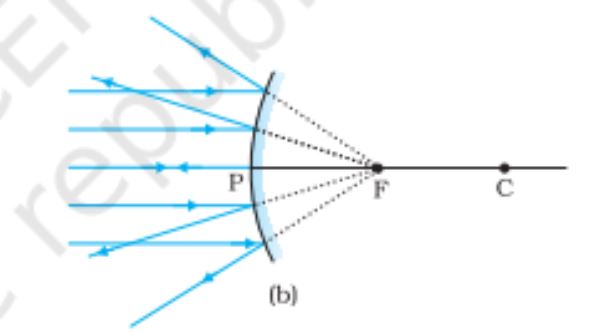
Convex mirror when rays are paraxial
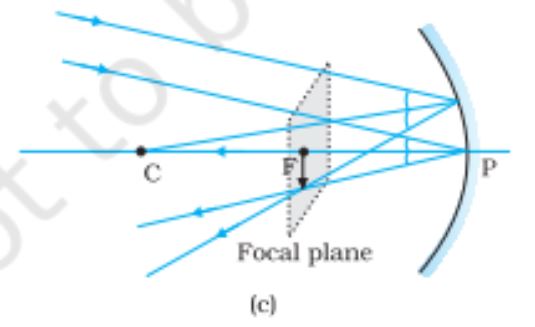
Formation of Focal Plane
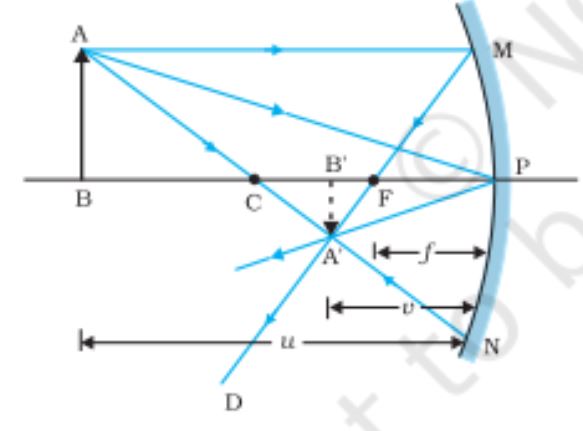
Image formation by a concave mirror
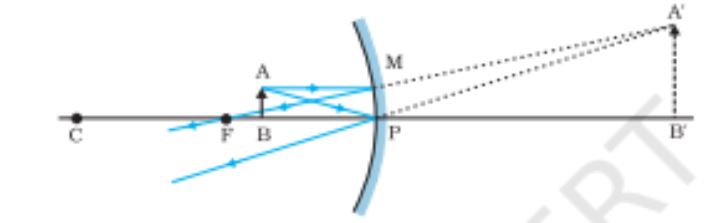
Image formation by a concave mirror with object between P and F
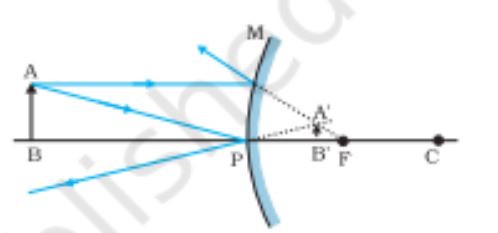
Image formation by a convex mirror
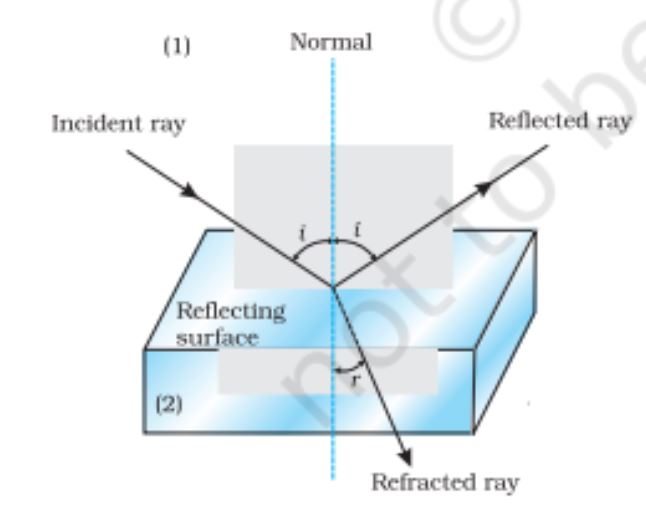
Refraction of light
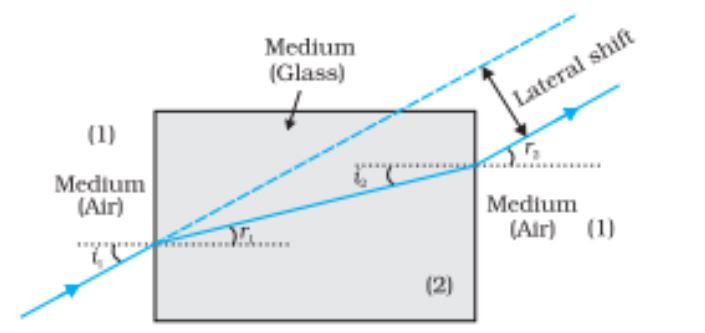
Lateral shift of a ray refracted through a parallel-sided lab
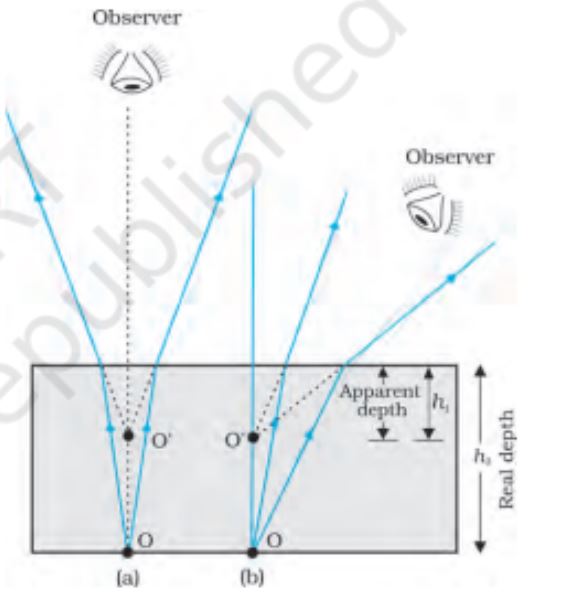
Apparent depth for a)normal viewing b)oblique viewing
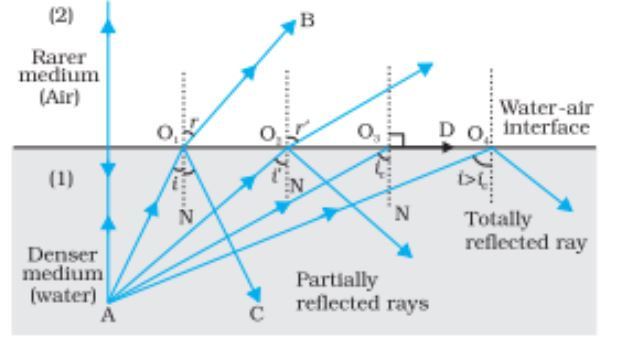
Total Internal Reflection
Refraction at a spherical surface
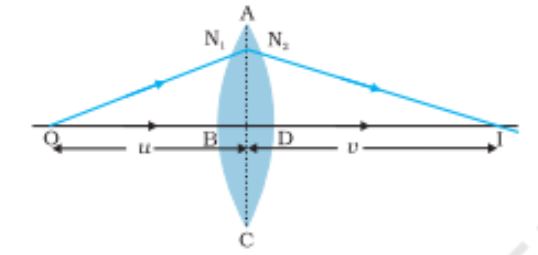
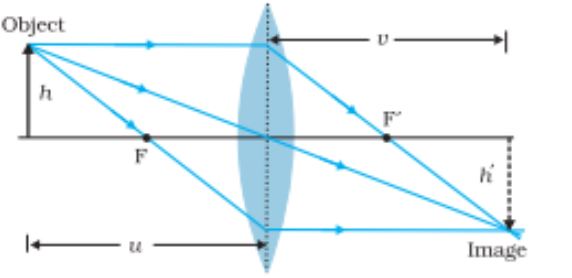
Position of object and image formed by a double convex lens
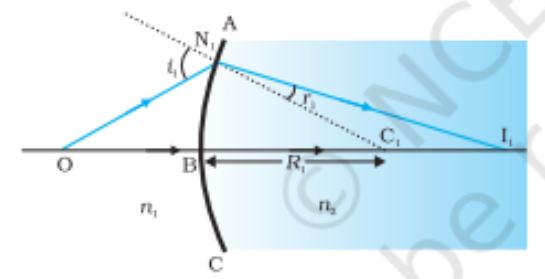
Refraction at the first spherical surface
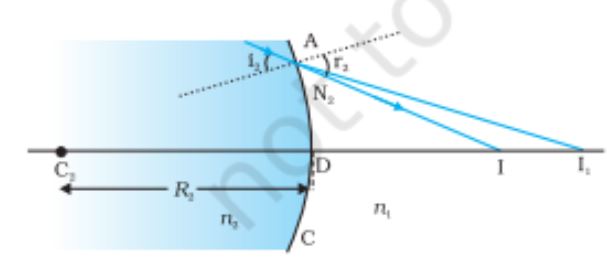
Refraction at the second spherical surface
Tracing rays through convex lens
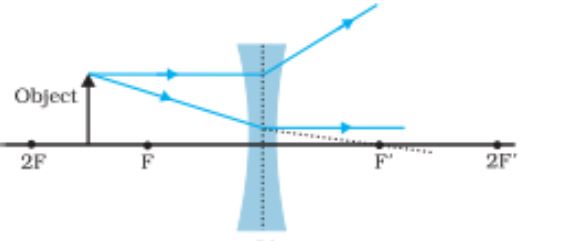
Concave Lens
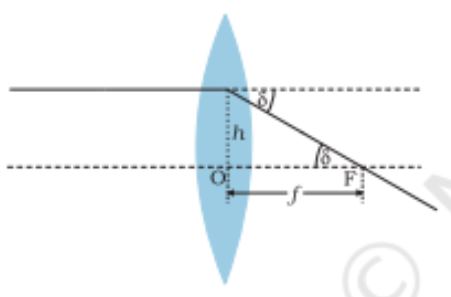
Power of a lens
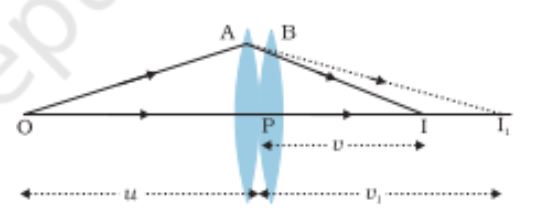
Image formation by a combination of two thin lenses in contact
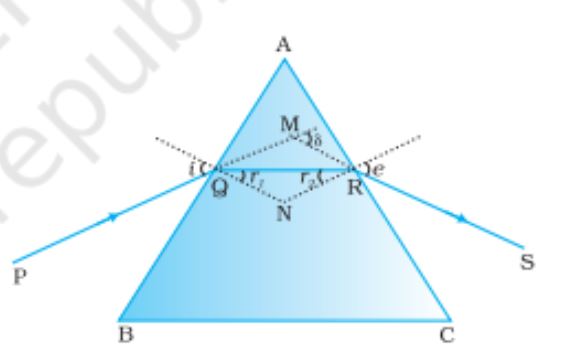
Refraction through a glass prism
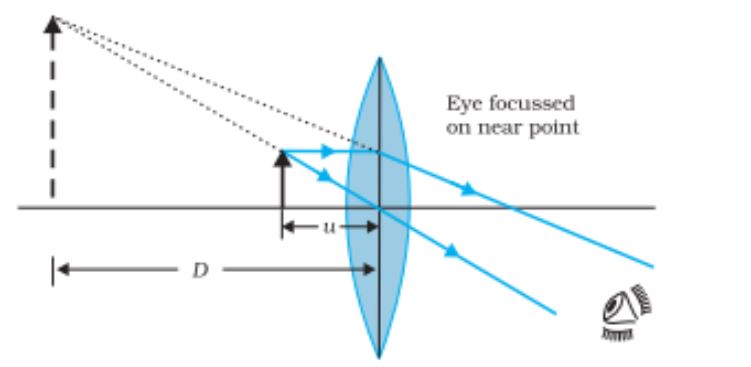
Simple Microscope, magnifying glass is located such that the image is at the near point
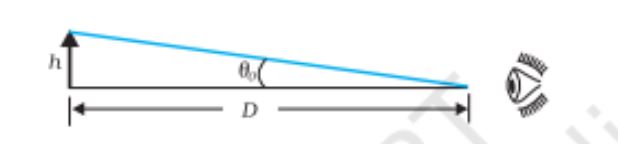
Simple Microscope, the angle subtended by the object is same as that of the near point
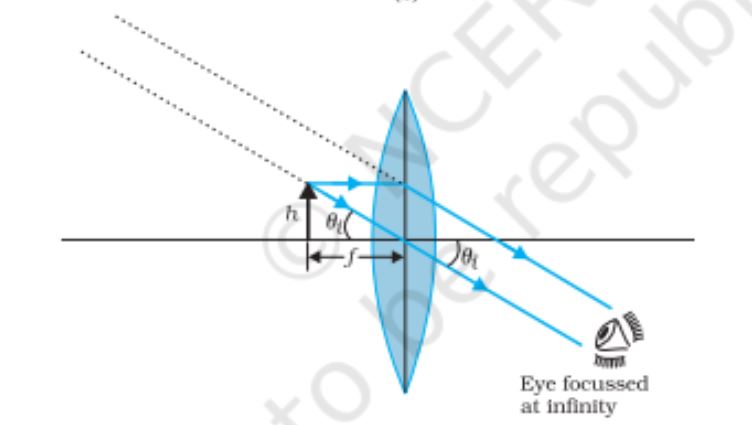
Simple Microscope, the object near the focal point of the lens, the image is far off but closer than infinity
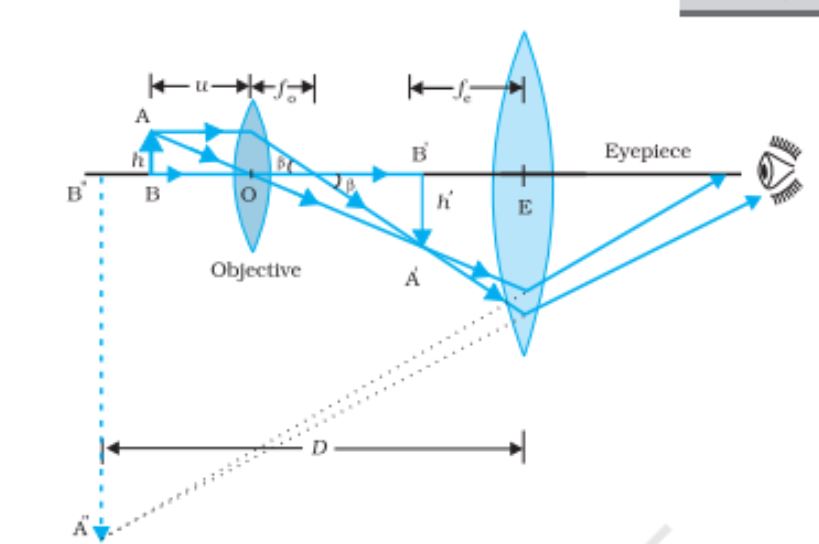
Formation of image by compound microscope
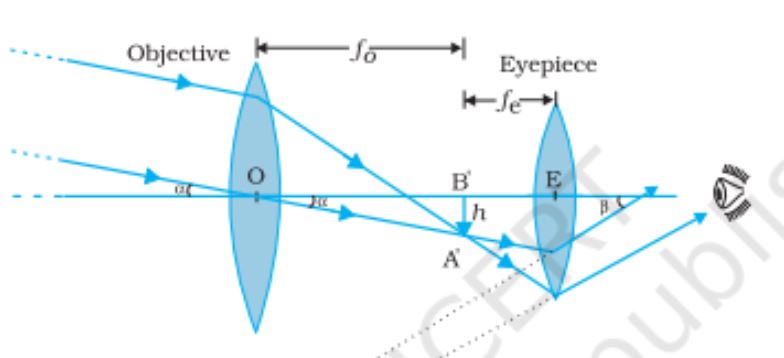
Refracting Telescope
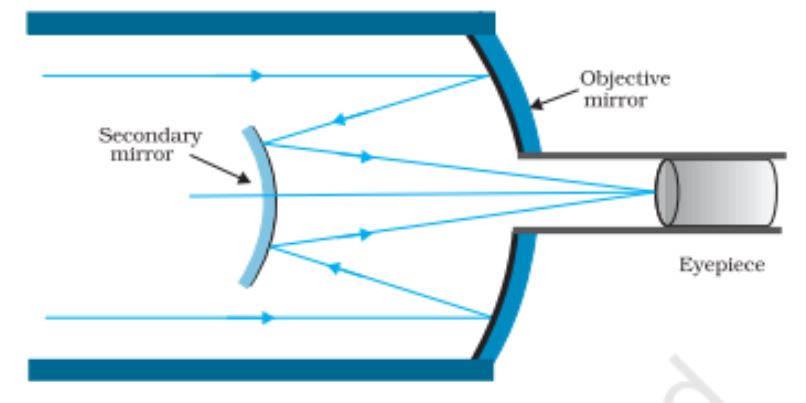
Reflecting Telescope (Cassegrain)
Important to Note:
Value of speed of light in vacuum (c)- 3 x 108 m/s
SI unit for the power of lens is Dioptre (D)
To download the Formula list and Ray Diagrams for CBSE Class 12 Physics Chapter 9, Ray Optics and optical instruments, click on the link below
Also Find:
#CBSE #Class #Physics #Ray #Optics #Optical #Instruments #Formula #List #Ray #Diagrams