Jagran Josh
CBSE Class 10 Circles Notes: Short and handwritten notes for Class 10 Circles have been presented in this article for students of Class 10. A PDF download link has also been attached at the bottom of the article for your reference.
-(1).jpg)
Download PDF for CBSE Class 10 Chapter 10 Circles Notes
Circles Class 10 Notes: Students of Class 10 can now use various study materials to strengthen their preparation for the upcoming CBSE Class 10 Board Exam in 2024. Jagran Josh brings to you such reliable and essential study resources. In this article, you can find the revision notes for Class 10 Maths Chapter 10 Circles. A PDF download link for short notes on circles has also been attached for your reference. Students who find these notes important can save them for future use.
Revision notes are quite important for students since they save a lot of time during practice sessions and revision at the time of examination. Additionally, it is said that any information gets stored in your brain for a longer duration of time if it has been written down once. Hence, we would advise all students of Class 10 to make notes while reading the chapters or at least refer to the ones brought to you by us.
CBSE Class 10 Circles Revision Notes
Find the revision notes for CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 10 Circles here. You can also refer to the PDF download link attached below to save these short notes for future reference.
- Circle– A circle is a collection of all points in a plane that are at a constant distance (radius) from a fixed point (center).
- Non-intersecting line– When the line does not intersect with respect to the circle, it is known as a non-intersecting line.
- Secant line– When the line has two common points with the circle, it is called a secant line.
- Tangent– When the line intersects at one common point with the circle, it is called a tangent.
- There is only one tangent at a point of the circle
- The tangent to a circle is a special case of the secant when the two endpoints of its corresponding chord coincide
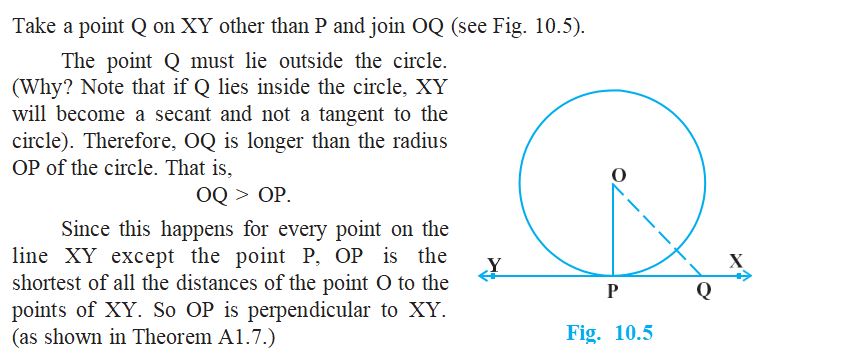
- Theorem– The tangent at any point of a circle is perpendicular to the radius through the point of contact.
- The theorem concludes that the line containing the radius through the point of contact is also sometimes called the ‘normal’ to the circle at the point.
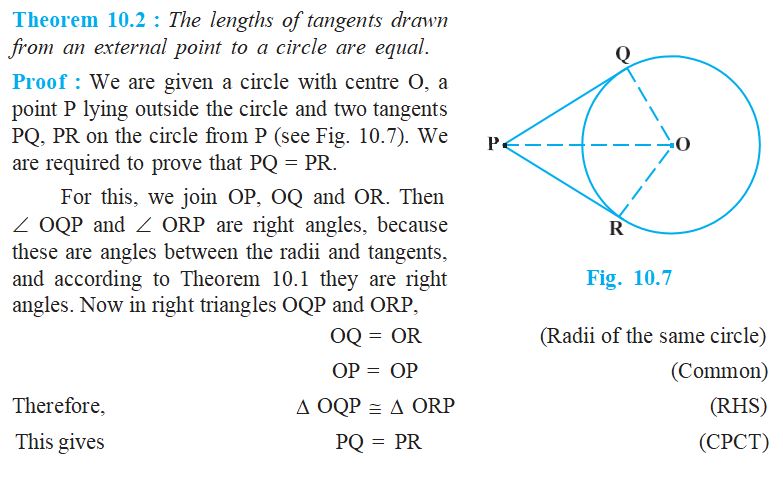
- Length of the tangent– The length of the segment of the tangent from the external point P and the point of contact with the circle is called the length of the tangent
- Theorem– The lengths of tangents drawn from an external point to a circle are equal
- Remarks from the theorem: (i) The theorem can also be proved by using the Pythagoras Theorem as follows:PQ2 = OP2 – OQ2 = OP2 – OR2 = PR2 (As OQ = OR) which gives PQ = PR. (ii) Note also that Ð OPQ = Ð OPR. Therefore, OP is the angle bisector of Ð QPR, i.e., the center lies on the bisector of the angle between the two tangents.
For complete Class 10 Circles Short Notes, click on the link below
Also Check:
CBSE Class 10 Mathematics Syllabus 2023-2024
CBSE Class 10 Mathematics Sample Paper 2023-2024
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Mathematics
Revision Notes for Class 10 Mathematics Real Numbers
Revision Notes for Class 10 Mathematics Polynomials
Revision Notes for Class 10 Mathematics Pair of Linear Equations In Two Variables
Revision Notes for Class 10 Mathematics Quadratic Equations
Revision Notes for Class 10 Mathematics Arithmetic Progressions
#Circles #Class #Notes #CBSE #10th #Mathematics #Chapter #Download #PDF