Jagran Josh
HPBOSE Class 11 Chemistry Syllabus 2023-24: The Himachal Pradesh Board of School Education (HPBOSE) has released the official syllabus for class 11 for the academic session 2023-24. This syllabus includes a detailed list of unit-wise topics along with the weightage distribution. It also mentions the details of internal assessment and practical exam. In this article, we have mentioned the detailed syllabus for you to know the complete course structure, course contents and examination details. You can also check the question paper design for the annual exam to be held in 2024. Download the full syllabus in PDF here.
HP Board Class 11 Chemistry Syllabus 2023-24
COURSE STRUCTURE
|
Unit No. |
Unit Name |
Marks |
|
Unit I |
Some basic Concepts of Chemistry |
3 |
|
Unit II |
Structure of Atom |
5 |
|
Unit III |
Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties |
3 |
|
Unit IV |
Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure |
5 |
|
Unit V |
States of Matter : Gases and Liquids |
3 |
|
Unit VI |
Thermodynamics |
5 |
|
Unit VII |
Equilibrium |
6 |
|
Unit VIII |
Redox Reactions |
3 |
|
Unit IX |
Hydrogen |
3 |
|
Unit X |
S – Block Elements |
4 |
|
Unit XI |
Some P – Block Elements |
6 |
|
Unit XII |
Organic Chemistry – some basic Principles and Techniques |
5 |
|
Unit XIII |
Hydrocarbons |
7 |
|
Unit XIV |
Environmental Chemistry |
2 |
|
Total |
|
60 |
Course Content
Unit I: Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry
General Introdcution Importance and scope of chemistry
Historical approach to particulate nature of matter , laws of chemical combination . Dalton’s atomic theory concept of elements , atoms and molecules.
Atomic and molecular masses Mole concept and molar mass : percentage composition , empirical and molecular formula , chemical reactions , stoichiometry and calculations based on stoichiometry
Unit II: Structure of Atom
Discovery of electron . proton and neutron ; atomic number , isotopes and isobars.
Thomson’s model and its limitations Rutherford’s model and its limitations Bohr’s model and its limitations, concepts of shells and subshells , dual nature of matter and light , De Broglie’s
relationship . Heisenberg uncertainty principle , concept of orbitals , quantum numbers , shapes s. p. and d orbitals , rules for filling electrons in orbitals – Aufuau principle , Pauli exclusion principle and Hund’s rule , electronic configuration of atoms , stability of half filled and completely filled orbitals .
Unit III: Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties
Significance of classification , brief history of the development of periodic table , modern periodic law and the present form of periodic table , periodic trends in properties of elements – atomic radii , ionic radii , inert gas radii . lonization enthalpy , electron gain enthalpy, electronegativity , valence.
Unit IV: Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
Valence electrons , ionic bond , covalent bond : bond parameters . Lewis structure , polar character of covalent bond , covalent character of ionic bond , valence bond theory , resonance, geometry of covalent molecules , VSEPR theory , concept of hybridization , involving s.p and d orbitals and shapes of some simple molecules , molecular orbital : theory of homo nuclear diatomic molecules ( qualitative idea only ) , hydrogen bond.
Unit V: States of Matter : gases and liquids
Three states of matter. Intermolecular interactions , type of bonding, melting and boiling points.
Role of gas laws in elucidating the concept of the molecule , Boyle’s law . Charles law, Gay Lussac’s law , Avogadro’s law . Ideal behaviour , empirical derivation of gas equation,
Avogadro’s number. Ideal gas equation. Derivation from ideal behaviour, liquefaction of gases, critical temperature
Liquid State – Vapour pressure , viscosity and surface tension ( qualitative idea only, no mathematical derivations )
Liquid State – Vapour pressure , viscosity and surface tension ( qualitative idea only , no mathematical derivations ).
Unit VI : Thermodynamics
Concepts of System , types of systems , surroundings . Work , heat , energy , extensive and intensive properties , state fucntions .
First law of thermodynamics – internal energy and enthalpy , heat capacity and specific heat , measurement of AU and AH, Hess’s law of constant heat summation enthalpy of bond
dissociation combustion formation, atomization, sublimation Phase transition , ionization , and dilution.
Introduction of entropy as a state function , free energy change for spontaneous and non – spontaneous process, equilibrium Zeus
Unit VII : Equilibrium
Equilibrium in physical and chemical processes , dynamic nature of equilibrium , law of
mass action , equilibrium constant, factors affecting equlibrium- Le Chatelier’s principle ; ionic
equilibrium – ionization of acids and bases, strong and weak electrolytes , degree of ionization ,
concept of pH. Hydrolysis of salts ( elementary idea ) . Buffer solutions solubility product ,
common ion effect ( with illustrative examples )
Unit VIII : Redox Reactions
Concept of oxidation and reduction, redox reactions, oxidation number balancing redox reactions, applications of redox reactions
Unit IX : Hydrogen
Position of hydrogen in periodic table. occurrence, isotopes preparation, properties and uses of hydrogen; hydrides – ionic , covalent and interstitial; physical and chemical properties of water, heavy water, hydroen peroxide – preparation, reactions and structure; hydrogen as a fuel.
Unit X : S – Block Elements ( Alkali and Alkaline earth metals)
Group 1 and Group – 2 elements
General introduction , electronic configuration , occurrence , anomalous properties of the first element of each group, diagonal relationship, trends in the variation of properties ( such as ionization enthalpy. atomic and ionic radii). trends in chemical reactivity with oxygen, water, hydrogen and halogens: uses,
Preparation and properties of some important compounds :
Sodium carbonate , sodium chloride , sodium hydroxide and sodium hydrogen carbonate, biological importance of sodium and potassium
CaO, CaCO3 and industrial use of lime and limestone, biological importance of Mg and Ca.
Unit XI : Some P – Block Elements
General Introduction to P – Block Elements
Group 13 elements: General introduction , electronic configuration , occurrence . Variation of properties , oxidation states , trends in chemical reactivity , anomalous properties of first element of the group: boron – physical and chemical properties , some important compounds: borax , boric acids , boron hydrides . Aluminium uses , reactions with acids and alkalies.
Group 14 elements: General introduction , electronic configuration , occurrence , variation of properties , oxidation states , trends in chemical reactivity , anomalous behaviour of first element, Carbon – catenation, allotropic forms, physical and chemical properties, uses of some important compounds • oxides .
Important compounds of silicon and a few uses : silicon tetrachloride , silicones , silicates and zeolites .
Unit XII : Organic Chemistry – Some Basic Principles and Techniques
General introduction method qualitative and quantitative analysis, classifiction and IUPAC nomenclature of organic compounds.
Electronic displacements in a covalent bond: inductive effect, electromeric effect, resonance and hyper conjugation.
Homolytic and heterolytic fission of a covalent bond: free radicals carbocations, carbanions, electrophiles and nucleophiles , types of organic reactions
Unit XIII : Hydrocarbons
Classification of Hydrocarbons
Alkanes – Nomenclature, isomerism, conformations ( ethane only ), physical properties, chemical reactions including free radical mechanism on halogenation, combustion and pyrolysis . Alkenes Nomenclature, structure of double bond (ethene ) geometrical isomerism,
physical properties, methods of preparation; chemical reactions: addition of hydrogen, halogen , water, hydrogen halides (Markovníkov’s addition and peroxide effect). ozonolysis, oxidation , mechanism of electrophilic addition.
Alkenes – Nomenclature , structure of triple bond ( ethyne ) . physical properties .
Methods of preparation , chemical reactions : acidic character of alkynes , addition reaction of hydrogen , halogens , hydrogen halides and water .
Aromatic hydrocarbons: Introduction , IUPAC nomenclature , Benzene : resonance aromaticity , chemical properties : machanism of electrophilic substitution. – nitration sulphonation , halogenation . Friedel Craft’s alkylation and acylation directive influence of functional group in mono – substituted benzene , carcinogenicity and toxicity .
Unit XIV : Environmental Chemistry
Environmental pollution – air , water and soil pollution , chemical reactions in atomosphere smog, major atmospherica pollutants ; acid rain, ozone and its reactions , effects of depletion of ozone layer, greenhouse effect and global warming – pollution due to industrial wastes : green chemistry as an alternative tool for reducing pollution , strategy for control of environmental pollution.
PRACTICALS
|
Evaluation Scheme for Examination |
Marks |
|
Volumetric Analysis |
06 Marks |
|
Salt Analysis |
05 Marks |
|
Content Based Experiment |
03 Marks |
|
Class Record and Viva |
03 Marks |
|
Investigatory Project |
03 Marks |
|
Total |
20 Marks |
To check the contents and experiments prescribed for practicals, download the full syllabus from the following link:
|
HP Board Class 11 Chemistry Syllabus 2023-24 (PDF) |
HP Board Class 11 Chemistry Exam Pattern and Marking Scheme 2024
|
Chemistry (Theory) |
60 Marks |
|
Practical |
20 Marks |
|
Internal Assessment |
20 Marks |
|
Total |
100 Marks |
Design of Question Paper
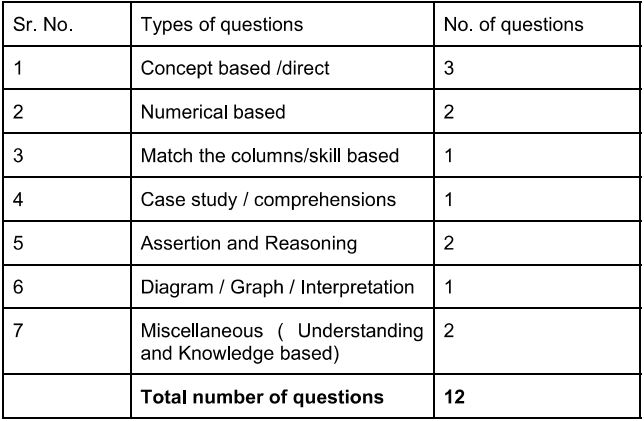
Total No. of Questions: 30
a) Section A Q.1 to Q. 12 MCQ (1 mark)
b) Section B Q. 13 to Q. 21 short answer
c) Section C Q.22 to Q. 27 subjective
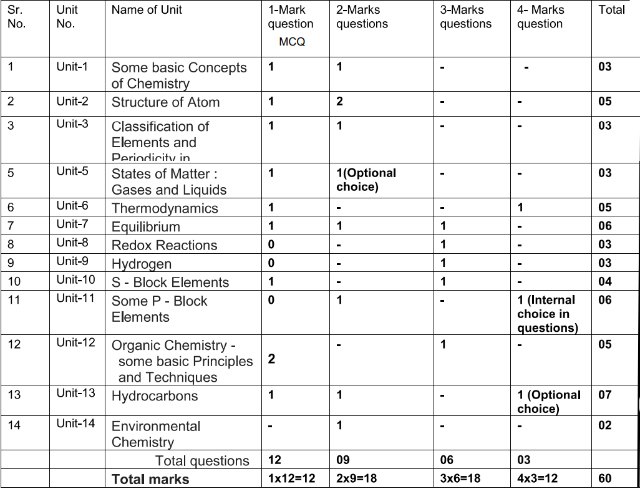
Blue Print of MCQs
Prescribed Book
Chemistry – Published by HPBOSE Dharamshala
#Board #Class #Chemistry #Syllabus #Marking #Scheme #Question #Paper #Design