Jagran Josh
Class 12 Biology Revision Notes 2023-24: Check CBSE Class 12 Biology short notes, revision notes, CBSE notes and NEET important notes for quick and effective revision. Get chapter-wise revision notes from subject matter experts.

Download CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 11 Organisms and Populations Revision Notes PDF
Organisms and Populations CBSE Notes: Revision notes are important support material for students to prepare for the exams. These revision notes are short notes on chapters, which help students go through the content in less time. Only the main things are highlighted in short notes with the help of flow charts and diagrams, along with some text.
In this article, you will find Class 12 biology revision notes. These are specifically designed for Chapter 11 Organisms and Populations CBSE notes. One can use these CBSE notes for Class 12 Biology Chapter 11 as notes for NEET 2024 and CBSE exam board Biology short notes. Topics like Organism and Its Environment, Major Abiotic Factors, and Responses to Abiotic Factors, which are not part of the revised NCERT Class 12 Biology textbook, are not included in the revision notes.
CBSE Class 12 Organisms and Populations Revision Notes
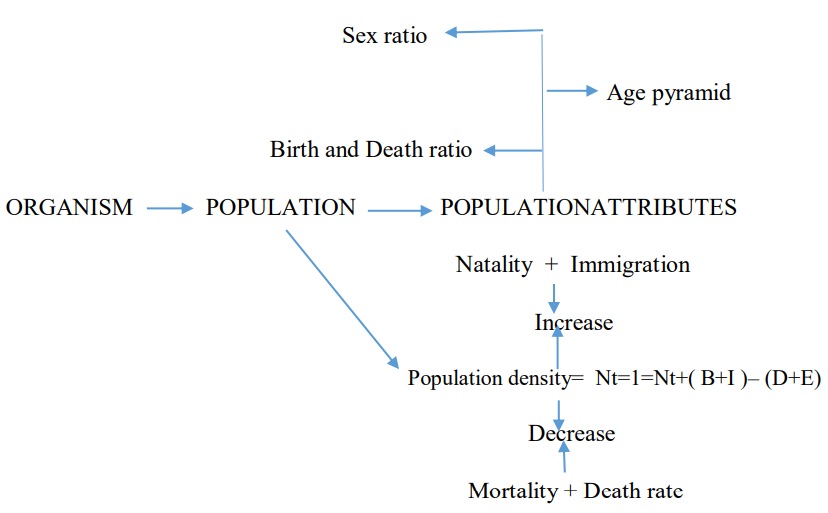
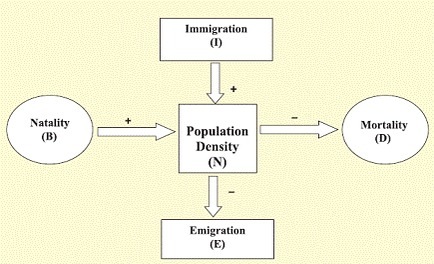
N= Population density
B= No. of births
I= No. of Immigrants
D= No. of deaths
E= No. of emigrants
You can see from the above equation that population density will increase if the number of births plus the number of immigrants (B + I) is more than the number of deaths plus the number of emigrants (D + E). Under normal conditions, births and deaths are the most important factors influencing population density, the other two factors assuming importance only under special conditions.
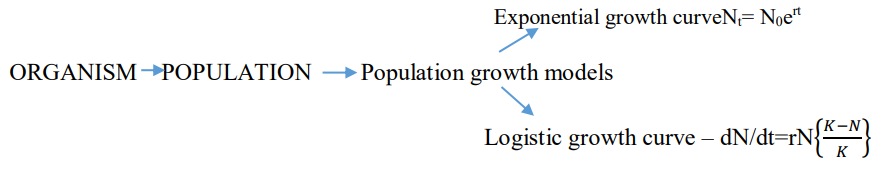
If in a population of size N, the birth rates (not total number but per capita births) are represented as b and death rates (again, per capita death rates) as d, then the increase or decrease in N during a unit time period t (dN/dt) will be
dN/dt = (b – d) × N
Let (b–d) = r,
then dN/dt = rN
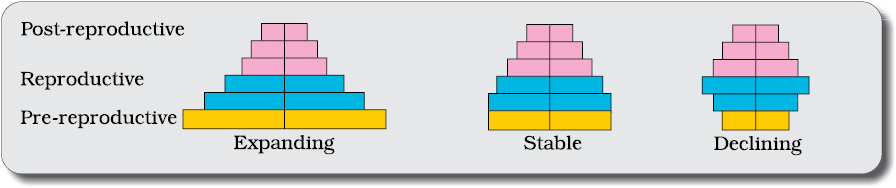
Age pyramid for human population
- Population – A population is defined as a group of individuals of the same species that live in a particular time.
- A population has certain attributes that an individual organism does not have. Individual may have births and deaths but a population has birth rates and death rates.
- Sex ratio is an another attributes of population. An individual may be male or female but population has sex ratio.
- A population at given time is composed of different individuals of different ages. If the age distribution is plotted for the population, the resulting structure is called age pyramid.
- Population Density is a measurement of population per unit area.
- Population growth – The main factors that determine the population growth are Natality- B ( number of births), Mortality- D ( number of deaths), Immigration – I ( individuals that come into habitat) and Emigration – E ( individuals that leave the habitat)
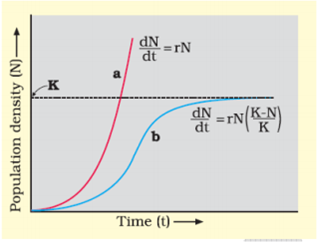
- Growth model- Exponential growth – This growth occurs when food and space is available in sufficient amount. The population grows in an exponential or geometric fashion.
- Logistic growth – There is a competition between the individuals of a population for food and space. The fittest organism survives and reproduces. In nature, a given habitat has enough resources to support a maximum possible number, beyond which no further growth is possible. This limit as nature’s carrying capacity(K) for that species in that habitat.
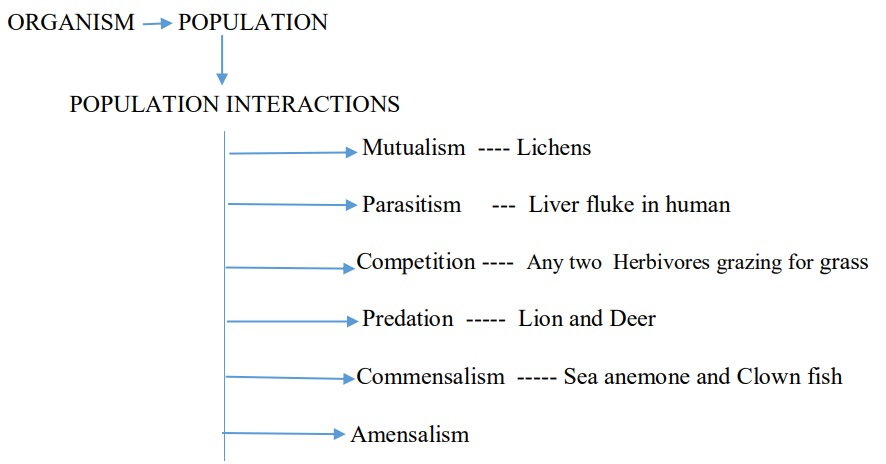
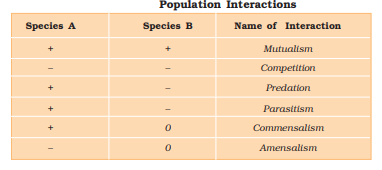
- Population Interaction – All animals, plants and microbes in a biological community interact with each other.
- These interactions may be beneficial, detrimental or neutral to one species or both.
i) Predation – It is the interaction between two species where one species dominates the other and feeds on its population.
ii) Parasitism – It is the relationship between two living organisms of different species where parasite obtains its food directly from another living organism (host).
iii) Competition– It is the rivalry between two or more organisms for obtaining the same resources.
iv) Mutualism – Interaction between two organisms of different species where both are benefited but cannot live separately.
v) Commensalism – It is the interaction in which one species benefit and the other is neither harmed nor benefitted.
Read:
Related:
#Organisms #Populations #Revision #Notes #CBSE #Class #Biology #Download #PDF


